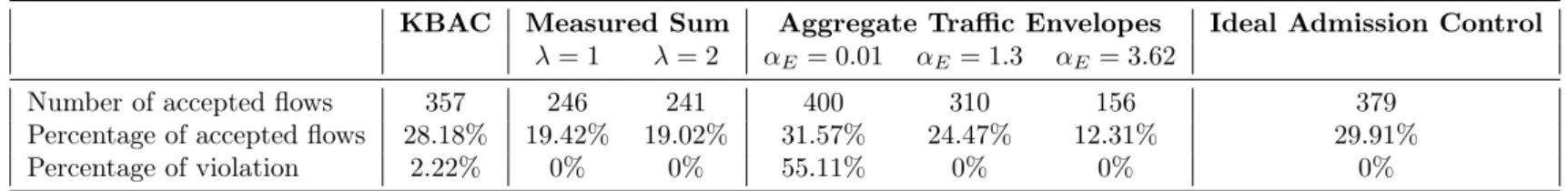
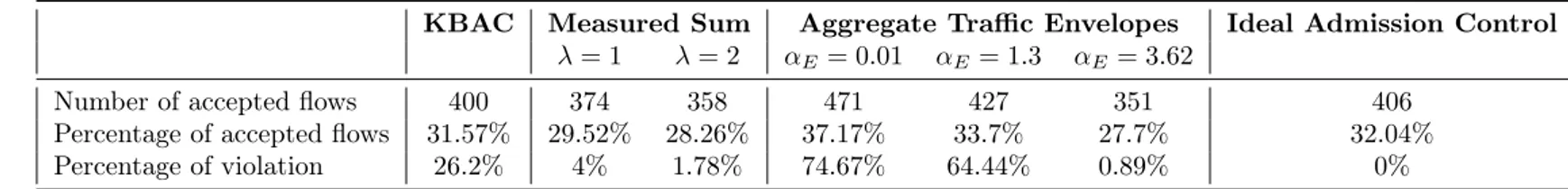
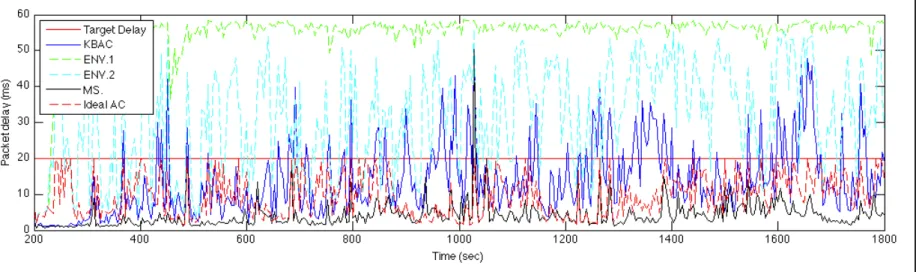
KBAC: Knowledge-Based Admission Control
Texte intégral
Figure
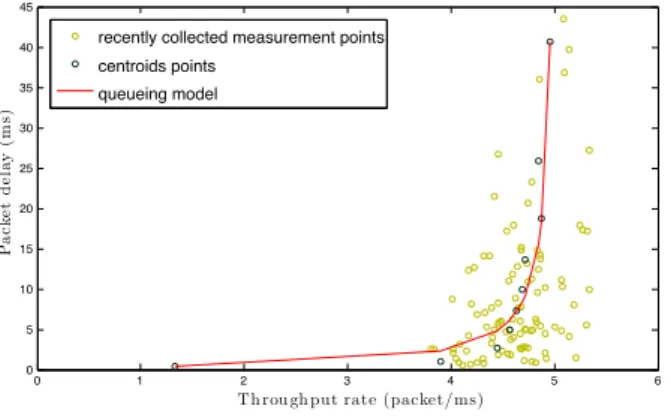
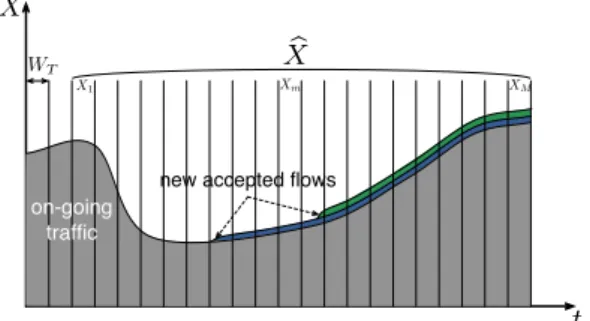

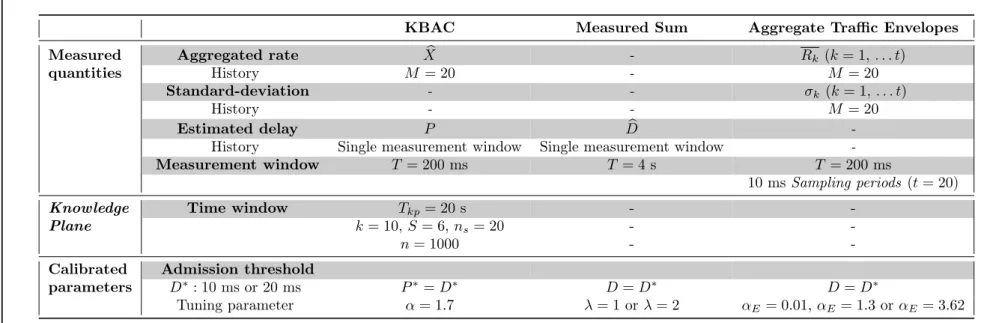
Documents relatifs
This paper presents an approach which has for objective to model new tools allowing to help the controllers to assume the incessant increase of the air traffic
Green Networking, Energy-Aware Networks, Admission Con- trol, Energy consumption, Routers, Network Simulator NS- 2, Traffic Class
- Au lieu de se synchroniser sur « l’accès à la donnée » comme dans le cas des mutex, les variables de condition permettent aux threads de synchroniser en fonction de la valeur de
Thus, in the individual optimization case, one could hope that by determining the signalling according to the value L that optimizes the socially optimal problem (in case of
However, the fact that a threshold policy is optimal implies that for optimally controlling arrivals we only need partial information - we need a signal to indicate whether the
Therefore, the higher cross-section measured from scan pair number five (see Fig. 40) cannot be explained by random beam drifts and the deviation from the average cross-section
In this paper we present a fuzzy reinforcement learning admission control approach based on the increasingly popular Pre-Congestion Notification framework that requires no a
Impact of turbulence closures and numerical errors for the optimization of flow control devices. Sum- mary of the 2004 Computational Fluid Dynam- ics Validation Workshop on