Limited capacity for ammonia removal by brain in chronic liver failure: potential role of nitric oxide
Texte intégral
Figure
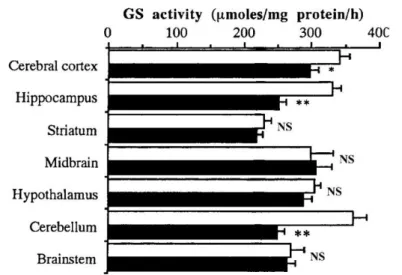
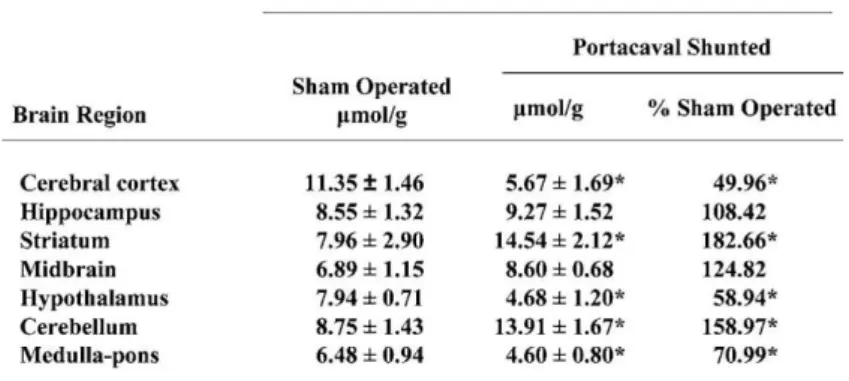
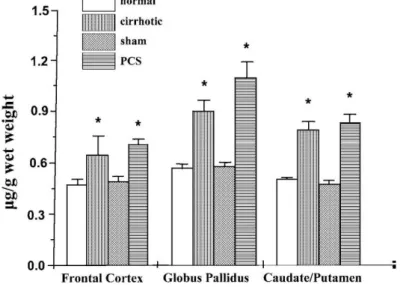
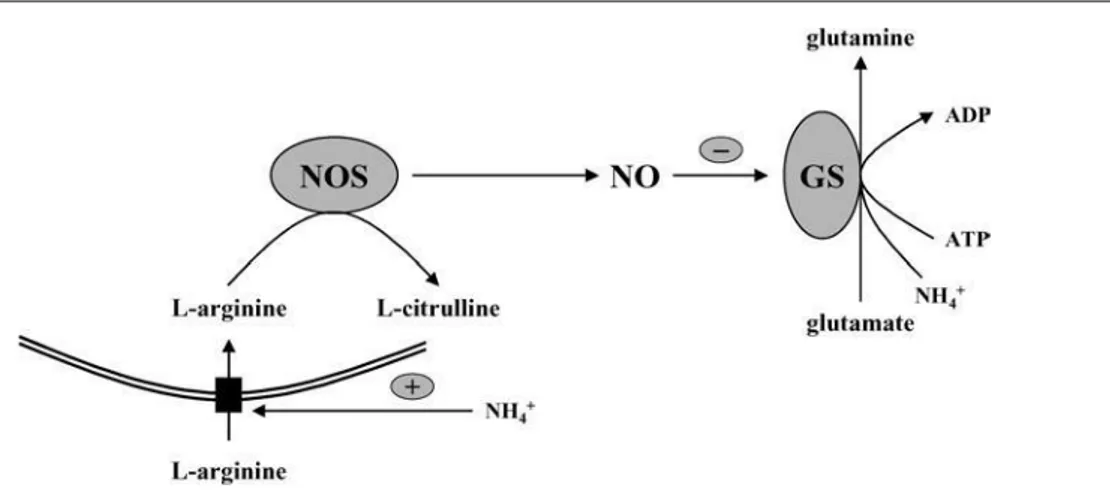
Documents relatifs
A experiência relatada apoiou-se na intervenção dos mediadores sociais da Extensão Pesqueira do Instituto Capixaba de Pesquisa, Assistência Técnica e Extensão
Á cet égardÀ cet égard, il est tout à fait pertinent de poser comme le fait Lila Le Trividic Harrache dans cet ouvrage, la question suivante : « dans quelle mesure l’entrée
la variable Valeur indiquant la charge normative dont est investie la solidarité. La pierre angulaire de la société moderne consistait en la division technique et sociale du
Now, using the compactness of all the minimizing sequences of ( 1.5 ) (which will be obtained along the proof of Theorem 2 in Section 2.2.2 ) and the uniqueness result given by
La deuxième motivation principale de la propagande du sport dans ces pays pourrait être en lien avec le « malaise dans la culture » qui trouverait sa solution
In conclusion, we reported the first example of desym- metrization of a centrosymmetric meso difor- myl[2.2]paracyclophane. Based on a highly enantioselective
Émanant de la société civile et en marge des processus institutionnels, l’urbanisme tactique propose la réalisation d’interventions urbaines de manière incrémentale en