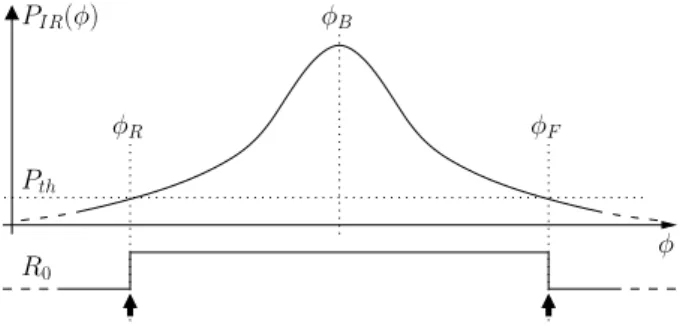
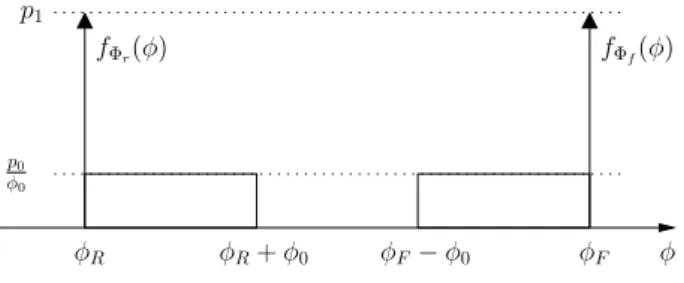
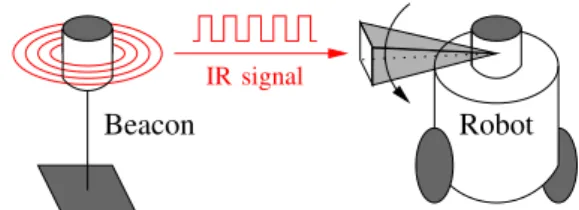
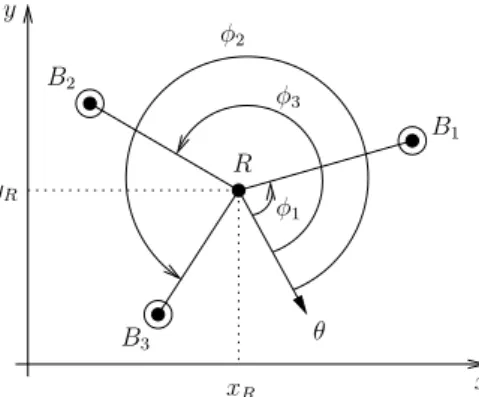
BeAMS: a Beacon based Angle Measurement Sensor for mobile robot positioning
Texte intégral
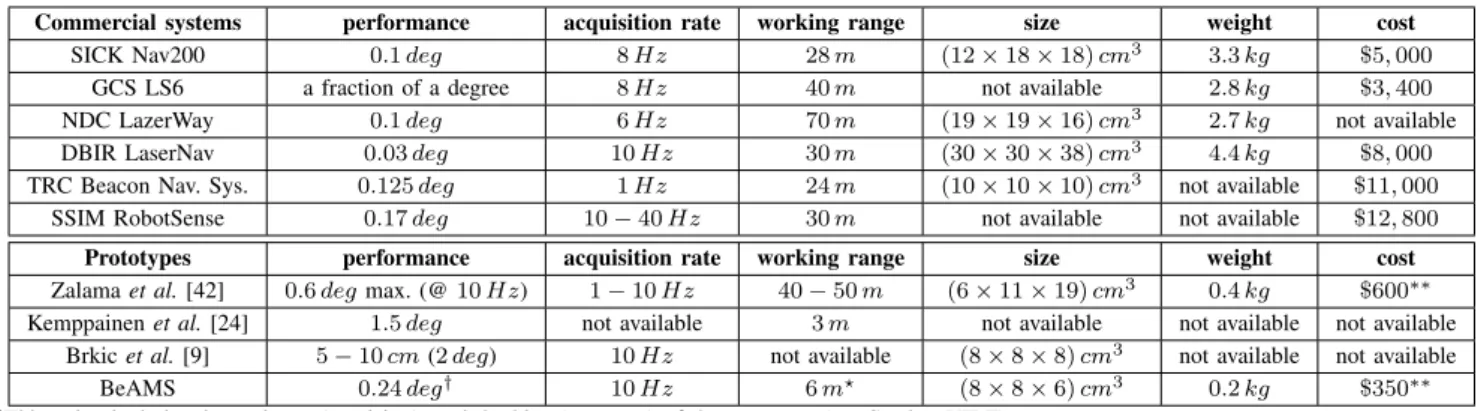
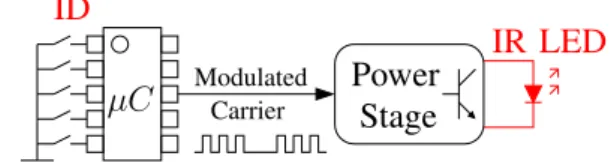
Figure
Documents relatifs
measurements of α and β , the landmarks position and the orientation of the robot to get an estimation of the velocities and of the position of the robot contrary to the EKF which
During all the calibration session, the thorax remains static and all upper limb movements are performed with respect to the thorax segment frame considered as a reference..
Geo-referenced noise measurements open the possibility to describe sound environments through advanced indicators, and characterize their temporal and
The interpretation of this expression is that the q th demodulated data symbol is equal to the transmitted data symbol affected by the channel distortion on the
High precision motion tracking is achieved by the combination of integral sliding mode control and time varying state feedback.. The main results are general and can be applied
The pose of the pattern has to be determined in the two frames using the Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm to minimize the error between estimated projection and projections
This was just a mirage, probably favoured by the well-known cross-linguistic similarities between singular mass and plural count, as well as by the occurrence of NCs
We have evidenced specific kinetic effects associated with the overlap of the T(LIESST), T(TIESST) and thermal hysteresis, which originate from a progressive stabilization of