Sunlight exposure during leisure activities and risk of prostate cancer in Montreal, Canada, 2005-2009
Texte intégral
Figure
Documents relatifs
While this article focuses on changes in women’s leisure activities following breast cancer and the associated social processes, it should also be noted that the effects of
7 In another case series, no congenital malformations were detected among 17 infants whose mothers took fluconazole for the treatment of vaginal candidiasis during pregnancy,
The overarching theme of the 2019 campaign was the achievement of the Lead Paint Alliance goal that all countries should have in place legally binding controls on the
For example, Bevil, O’Conner and Mattoon (1993) cites that older adults who reported a higher life satisfaction also reported the greatest number of recreation, leisure
The evidence reported in leisure studies has also suggested that digital technologies have altered leisure activities performed at home, and may also have changed the
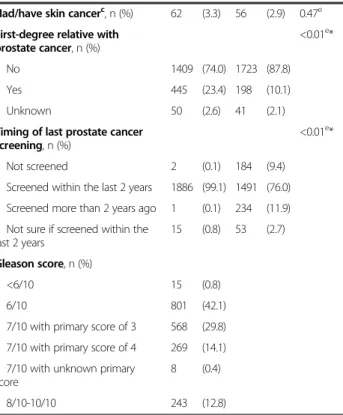
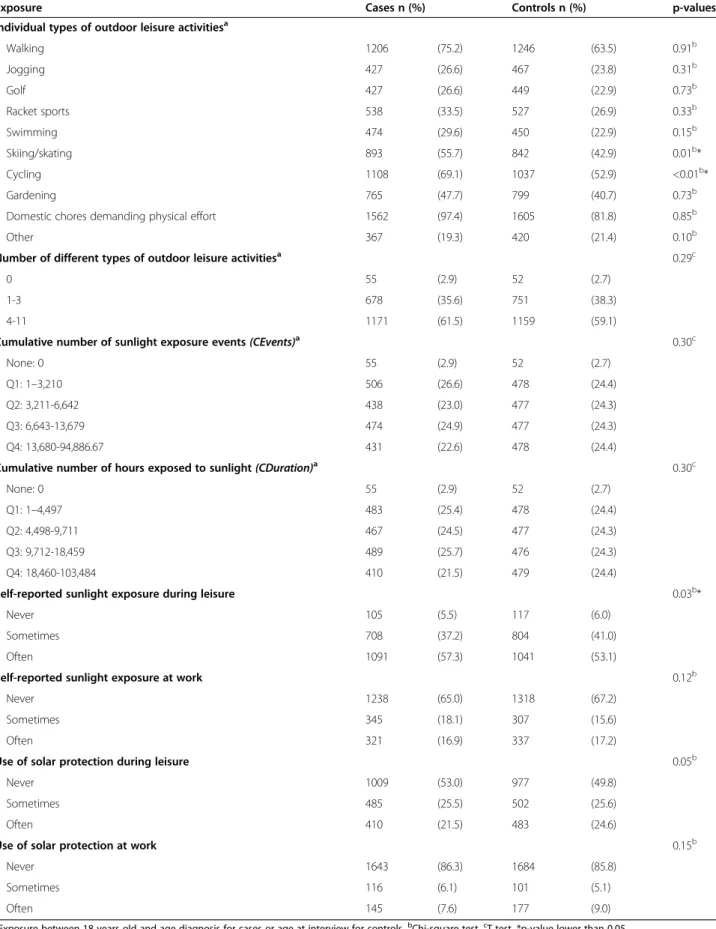
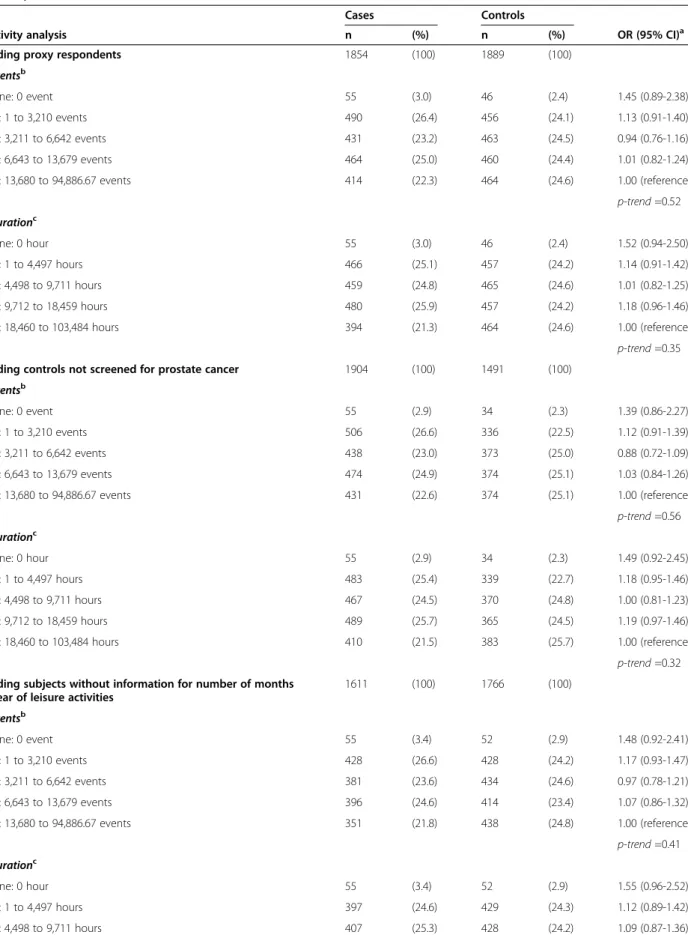
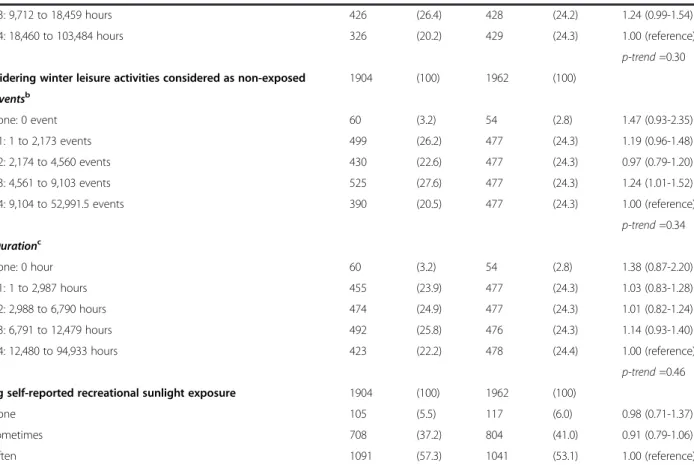
Individual-based exposure assessment methods used in previous studies include a self-reported recreational sun exposure level [16], a sun exposure index based on skin pigmentation
This present analysis found that only jobs involving the operation of transport equipment were associated with a signif- icantly elevated risk of prostate cancer (OR 5 1.90, 95%
Although no differences were found between the high self-determined profi le (high self-determined motivation and low non-self-determined motivation) and the additive profi le