Score Bounded Monte-Carlo Tree Search
Texte intégral
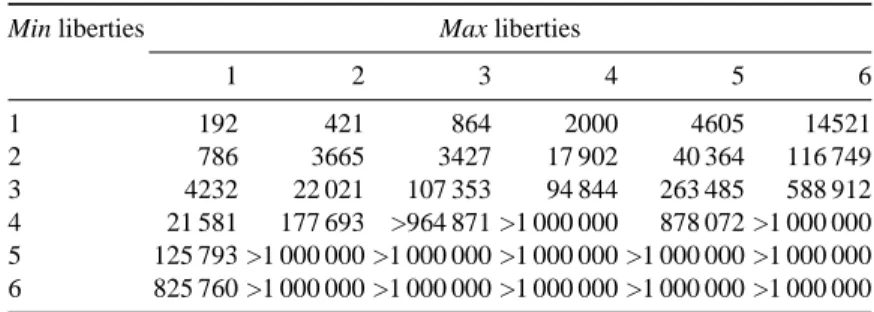
Figure
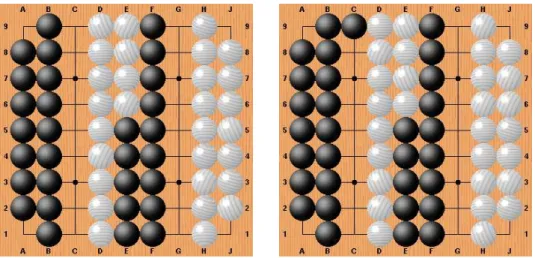
Documents relatifs
In automated reasoning, Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) has been applied to first-order automated theorem proving, using hand-crafted heuristics instead of neural networks [FKU17]..
In the classical POMCP algorithm, the value of a tree node is estimated based on sequences of UCB1 greedy ac- tion selections until a leaf node is reached, while POMCP-GO the
The random simulation done, the score received, MoGo updates the value at each node of the tree visited by the sequence of moves before the random simulation part.. Remark 1 In
In this paper, we propose a general scheme to embed in a flexible way feature generation in a wide range of tree-based supervised learning algorithms includ- ing single decision
In the classical POMCP algorithm, the value of a tree node is estimated based on sequences of UCB1 greedy ac- tion selections until a leaf node is reached, while POMCP-GO the
Monte-Carlo Tree Search and Reinforcement Learning for Reconfiguring Data Stream Processing on Edge Computing.. SBAC-PAD 2019 - International Symposium on Computer Architecture and
We will divide this section as follows: section 2.3.1 deals with the methods that simply try to approximate the value function itself, section 2.3.2 presents methods that aim
Once it leaves the Monte Carlo Tree, the roll-out phase generates the remaining moves according to the roll-out policy until the game reaches a final state.. The update phase