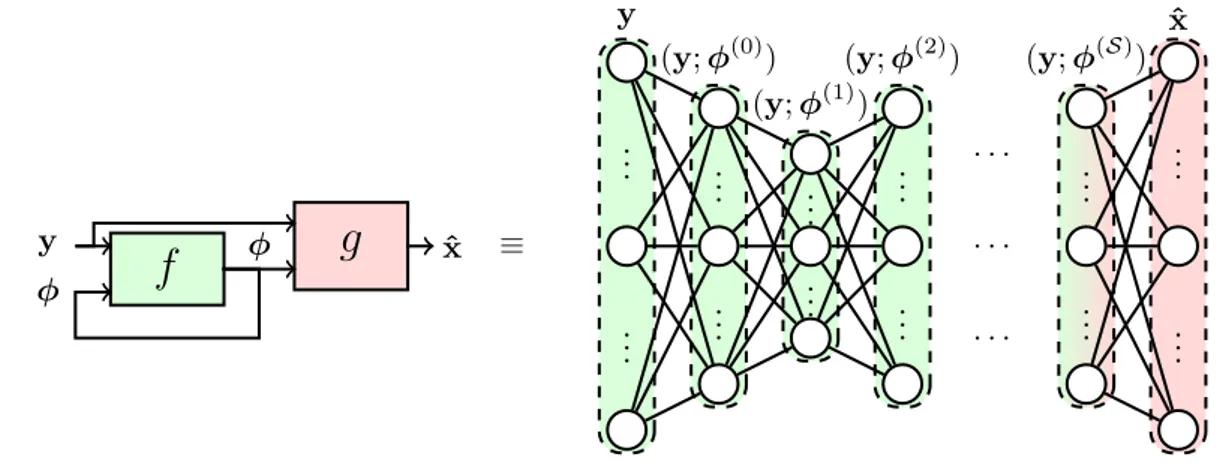
Advanced receivers for distributed cooperation in mobile ad hoc networks
Texte intégral
Figure




Documents relatifs
Conducted analysis has demonstrated that omitting two turbo demodulation iterations without decreasing the total number of turbo decoding iterations leads to promising
Our system is based on a trust graph, in which we have used a threshold cryptography scheme in order to resist against malicious nodes, that issue false public key certificates to
Interestingly, when the power imbalance is high, namely greater than 15 dB, the proposed code outperforms BHV, Srinath-Rajan and DjABBA codes and approaches 3D code which
Quality of service forest (QoS-F) is a distributed algorithm to construct a forest of high quality links (or nodes) from net- work point of view, and use these for routing
Smart Peering Selection reduces the number of adjacencies (as shown in Figure 4) while providing a connected set of adjacencies, but on the other hand does not generally provide a
We namely present multi- point relay (MPR) flooding and gateway flooding. We investigate the matter theoretically via mathematical modelling, as well as practically via simulations.
Performance of the MMSE IC-LE turbo equalizer as a function of the code rate Finally, Figures 10 and 11 present the performance of the MMSE turbo equalizer in EGPRS/MCS-8 and
The lowest power consumption of a FIR filter having a coefficient size of 4 bits and an input length of 16 bits is achieved when using poly-phase decomposition into eight



![Figure 2.11: A residual layer with 2 inner layers, for building residual networks [ He+16 ]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/2953492.80589/115.892.214.702.168.246/figure-residual-layer-inner-layers-building-residual-networks.webp)