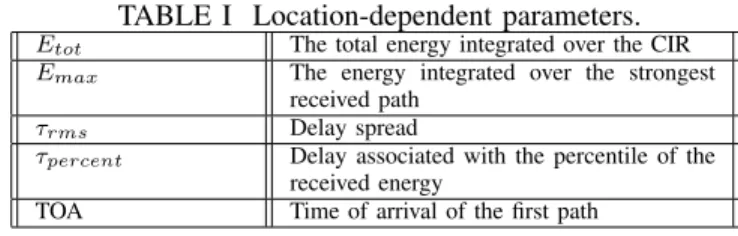
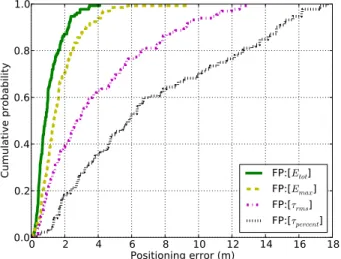
Fingerprinting localization based on neural networks and ultra-wideband signals
Texte intégral
Figure

Documents relatifs
We consider networks (1.1) defined on R with a limited number of neurons (r is fixed!) in a hidden layer and ask the following fair question: is it possible to construct a well
Although Tardos did not say anything on the key ideas supporting his code construction, we believe that his intuition was to render the scores as independent as possible from
The proposed method is compared to another well-known localization algorithm in the case of real data collected in an indoor environment where RSSI measures are affected by noise
In the final section, the results obtained with the proposed method are compared to the ones obtained when performing local- ization using connectivity information or the Weighted
For approbation of the program complex prototype performing additional training of Mask R-CNN (MRCNN) CNN architecture trained on COCO dataset was developed.. The
In the online phase, when getting a RSSI measurement with an unknown location at an unknown floor, we use a complete parallel network to determine the floor and then to estimate
The model consists of a convolutional network as image encoder, a recurrent network as natural language generator and another convolutional network as an adversarial
We prove that there exists an equivalence of categories of coherent D-modules when you consider the arithmetic D-modules introduced by Berthelot on a projective smooth formal scheme X
