Using Constraint Satisfaction Techniques and Variational Methods for Probabilistic Reasoning
Texte intégral
Figure


Documents relatifs
The main idea and benefit of belief graphical models is factoring a joint uncertainty measure in the form of a combination of local measures thanks to independence relations that
The experimental data is consequently used to rebuild different model parameters that define the gas/surface interaction of the different materials in question.. 2.1
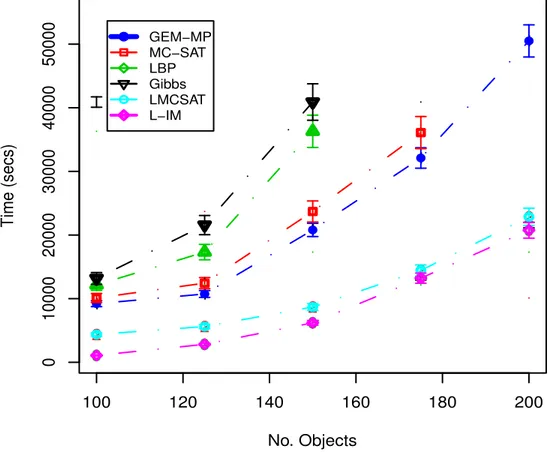
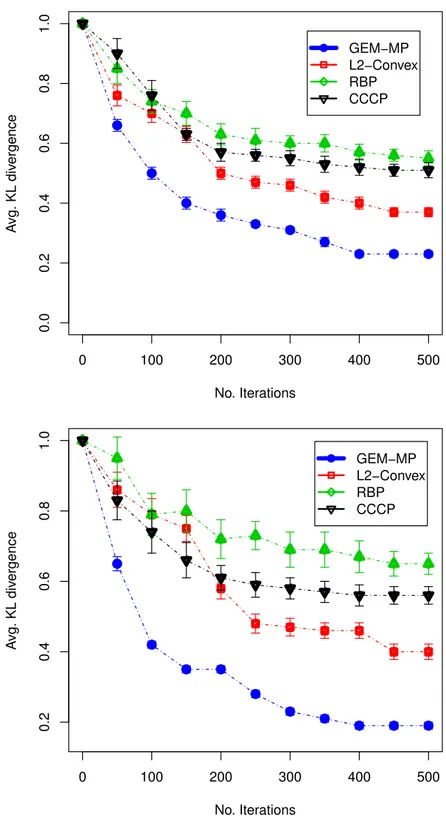
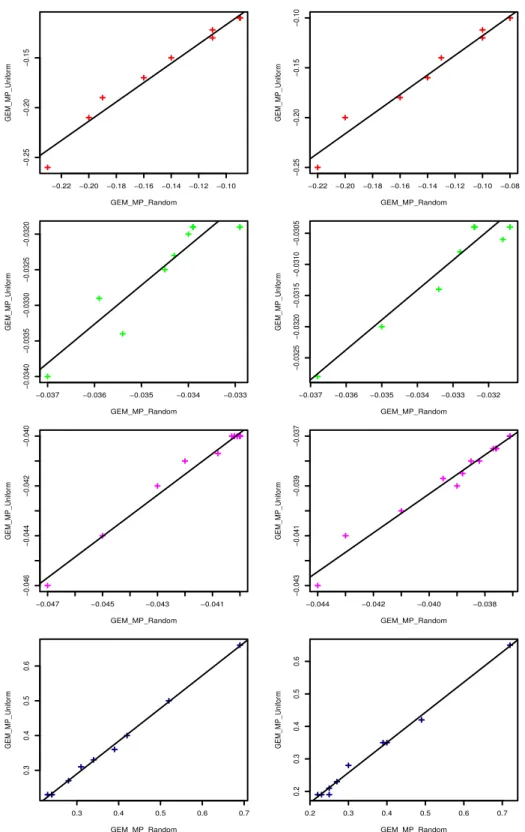
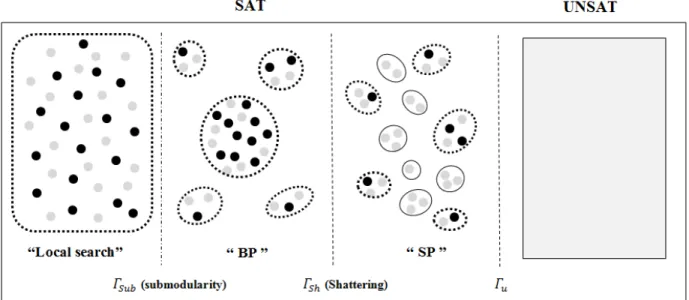
These upper bounds may then be jointly maximized with respect to a set, while minimized with respect to the graph, leading to a convex variational inference scheme for
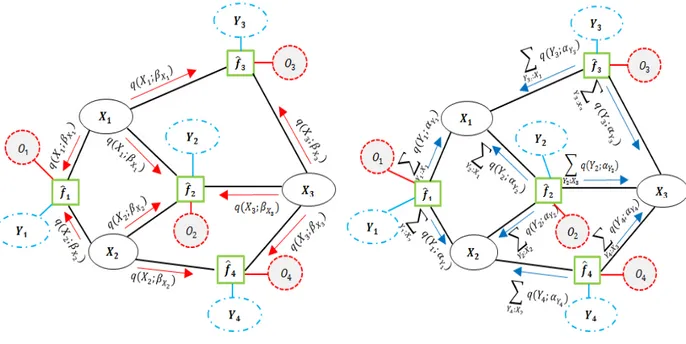
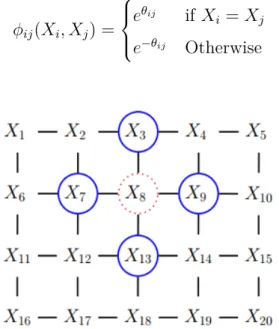
In this paper, we start by including all these models into a com- mon probabilistic model called the Pairwise Markov Model (PMM) [13]. This model has been introduced in a
Например, если преподаватель в алжирской аудитории для ознакомления учащихся с новым для них материалом по информатике остановывает свой выбор на
L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, Exact Bayesian Inference in
Modulation of HIV-1 replication in primary dendritic cells in contact with autologous CD4 T-lymphocytes Bin Su, Marina Elizabeth Biedma, Alexandre Lederle, Mélanie
We term this approach “SNIPE-based cosparse analysis AMP for imaging” (Scampi). We will detail the novel modifications of our approach with respect to GrAMPA in the sequel, but they