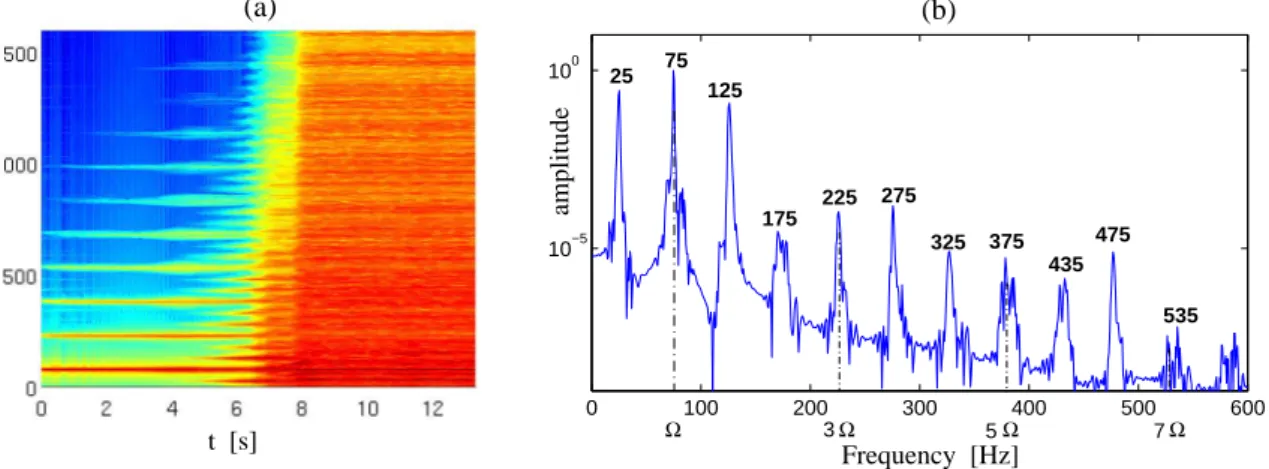
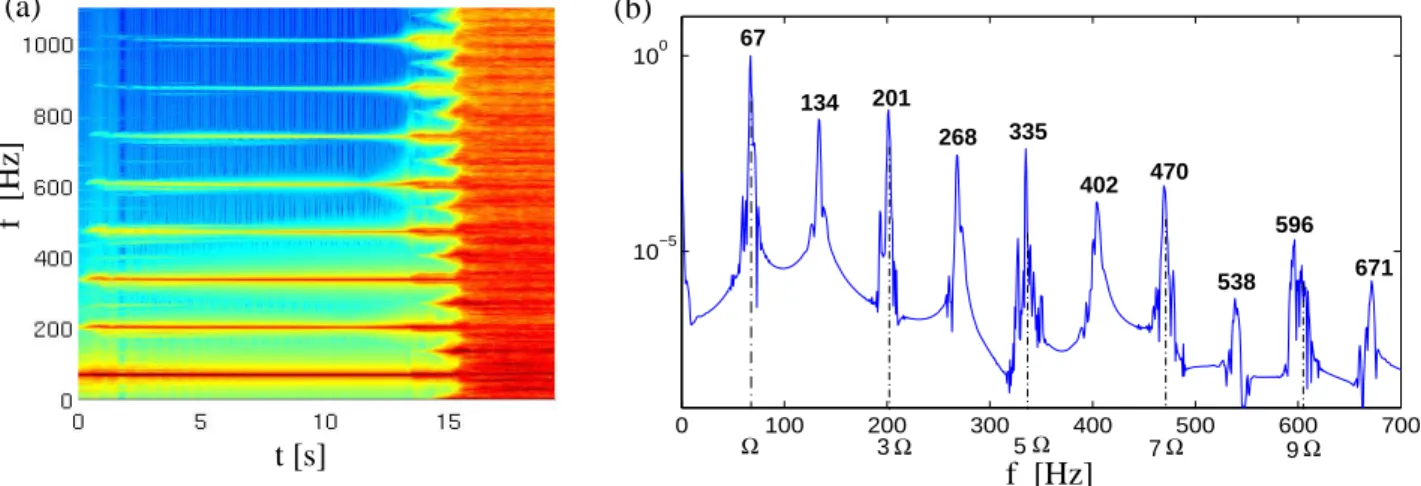
Transition scenario to turbulence in thin vibrating plates
Texte intégral
Figure
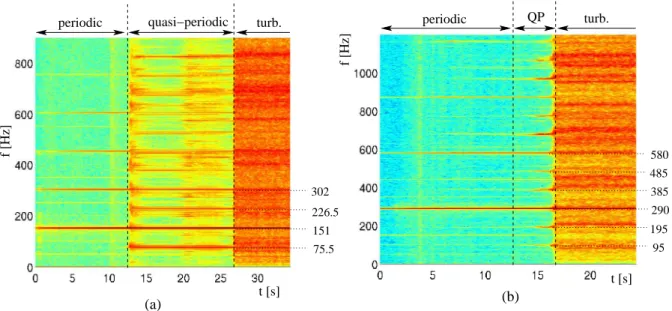



Documents relatifs
P.: A Kinetic Alfv´en Wave Cascade Subject to Collisionless Damping Cannot Reach Electron Scales in the Solar Wind at 1 AU, Astrophys. J., 712,
show the existence of a proton mode below 50 cm-1; the analysis shows that quantum effects and the proton coupling with an optic mode around 40 cm-1 play minor
2014 The threshold of the transition to turbulence of low Prandtl number convective flows occurs much closer to the convective threshold in an extended cylindrical cell,
A spectral analysis shows that this transition is dominated by two kinds of transfer: first, the shear instability induces a direct non-local transfer toward horizontal wavelengths
Right: Bifurcation diagram as ob- tained from the model in the same system (full line: average mean turbulent energy during the adiabatic decrease of Re; open and filled
• Principaux facteurs influençant les patrons de diversité des communautés de papillons urbains La partition hiérarchique met en avant deux facteurs majeurs influençant la
Taking the example of plane Couette flow, we discuss our current understanding of the transition to turbulence in globally subcritical systems, pointing out the specificity of the
intermediate species remain the same. We have also performed similar calculations with the free ATP molecule. Calculated Raman activities are reported in figure 4b and c. Figure 4: