MEG/EEG source imaging with a non-convex penalty in the time-frequency domain
Texte intégral
Figure
Documents relatifs
The results of our measurements for Na 2 colliding with Xe are shown in Fig, V-2 where the normalized rate constant is plotted versus the relative velocity vr
COMEDIE, a refractivity profile obtained by a radiosonde launch at station Payerne and data of the numerical weather model aLMo.. Panel (b) shows an irregular decrease of
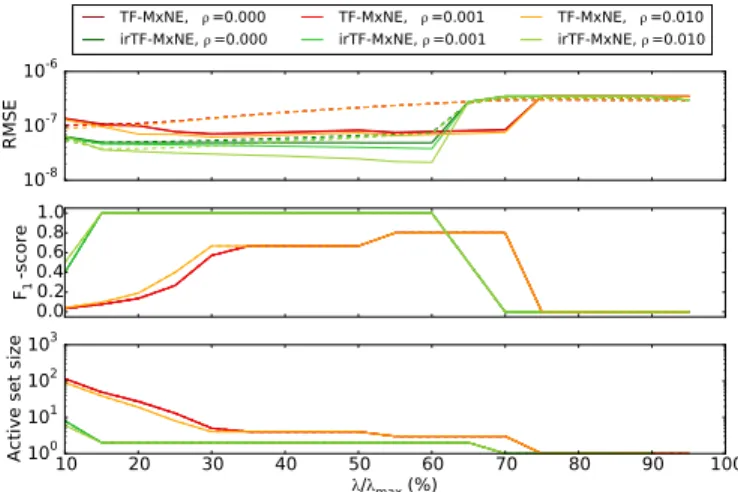
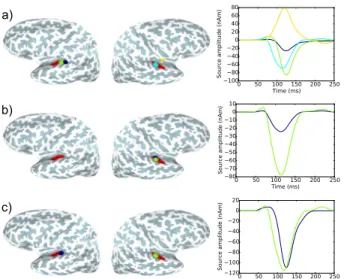
(5) A large regularization parameter λ space will lead to a spatially very sparse solution, while a large regularization parameter λ time will promote sources with smooth times
To go beyond this approach, we propose a solver where the sparsity of source configurations is promoted, but also where the time course of each active dipole is a linear combination
Elle ne trompait en tout cas pas Deluche qui l'entraîna, pour clore cette vi¬ site, dans la pièce que la vieille avait occupée auparavant, cham¬ bre meublée on ne peut plus sim¬
word initial Cs in Georgian considered as complex onsets: results confirm that indeed 2-3C clusters reflect a global, prototypical c-center coordination. however, when speech system
(c) Transition frequency (see text) as a function of azimuth and elevation in humans (left) and in the spherical model (right).. Normalized units converted
Ce mémoire consiste à étudier la croissance et les points …xes des solutions de certaines équations di¤érentielles linéaires du second ordre à coe¢ cients méromorphes.. Le