An exact method for the best case in a group sequence: Application to a general shop problem
Texte intégral
Figure
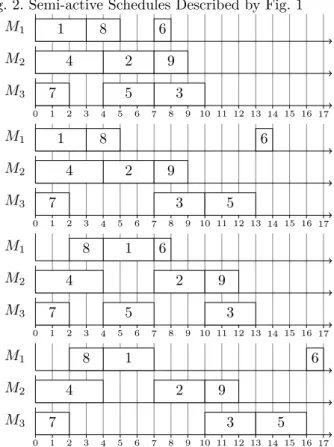


Documents relatifs
For the tribo-pairs, zirconia ðZrO 2 Þ and poly(tetrafluoroethylene) (PTFE) have been used in all permutations for both slider (pin) and track (disk), providing the four
For each percentage p of selected subsets in ERP1, we display: the number of solutions (#sol), the maximum size of a subset (n p ), the maximum number of subsets that cover an
Prise en charge des troubles du métabolisme minéral et osseux de la maladie rénale chronique. rise en charge
Finally, we present a hybrid branch-and- bound method to solve the problem, which performs, at each node, the satisfiability test and time-window adjustments and, when the domains
Technically, our main contribution is the following result, which gives a partial affirmative answer (in the special case of pseudo-Anosov 4-strand braids) to the Open Question 2
For each instance, we give the best found lower (LB1) and upper (UB1) bounds, the total number of branch and bound nodes (#nodes), the total CPU time in seconds (CPU), the initial
In other words, we want to reverse-engineer (3) and assess whether repulsive random variables as seen in random matrix theory can be a general device for variance reduction in
L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, émanant des