Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae induces SJPL cell cycle arrest in G2/M-phase and inhibits porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus replication
Texte intégral
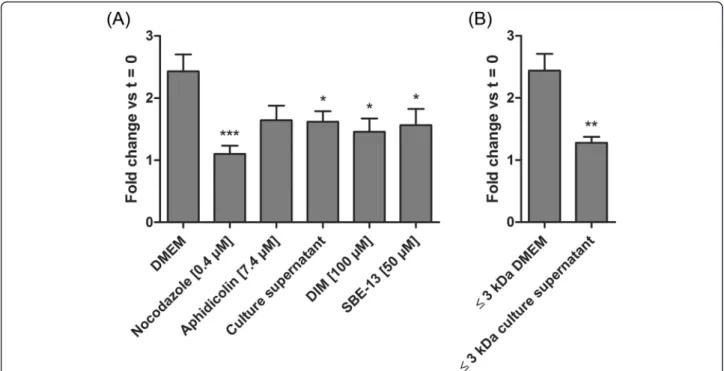
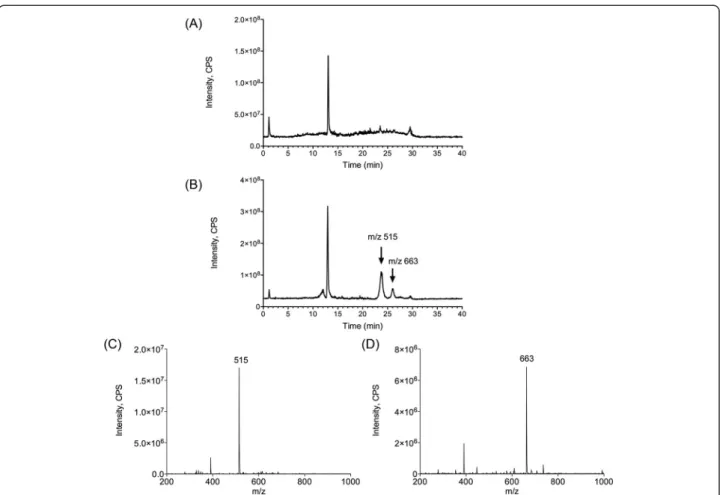
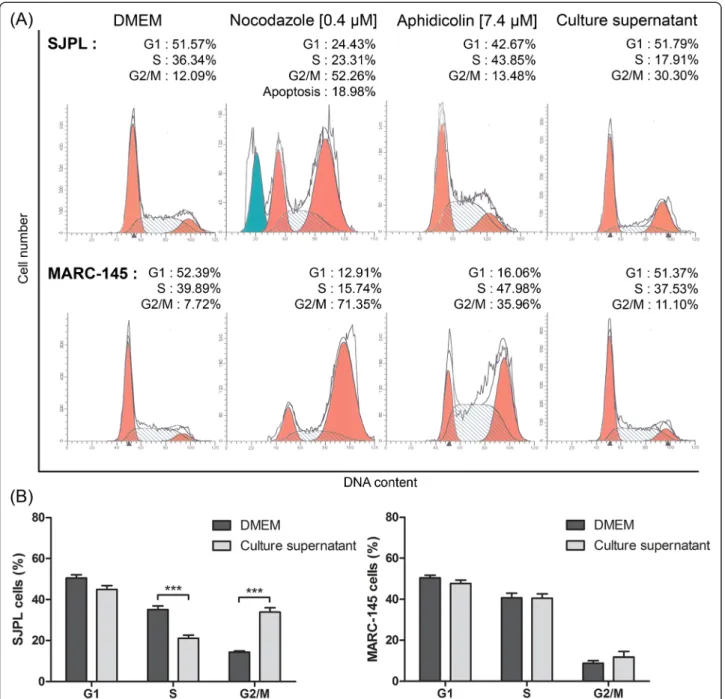
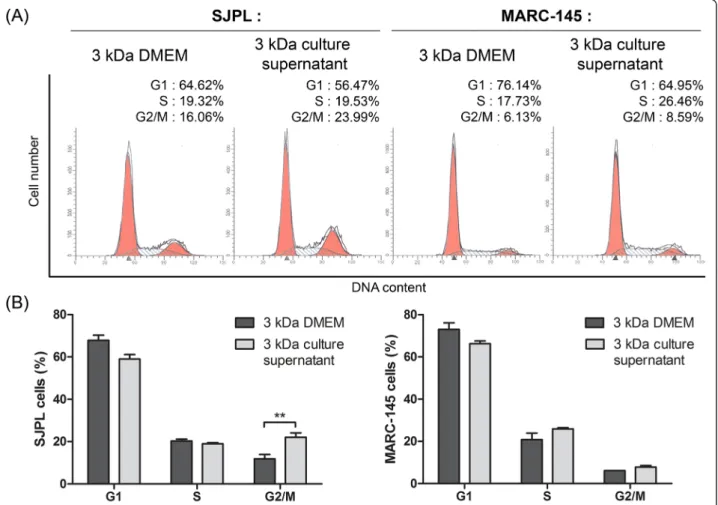
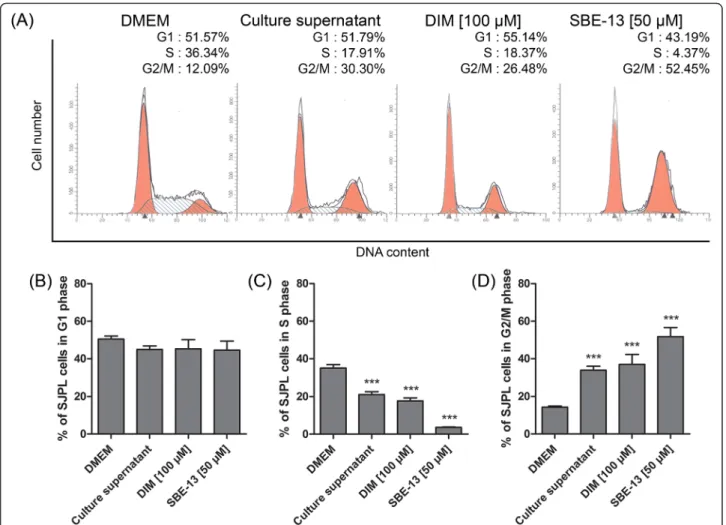
Figure

Documents relatifs
More specifically, the events of the FES associated with a network record their local history (namely the past actions of the involved participants), while the events of the
The optimization module runs external procedures which have been developed using a standard programming language to create the loaded meshing model, taking also
MURE 2 : SMURE, Serpent- MCNP Utility for Reactor Evolution User Guide -Version 1 Main Contributors.. [Technical Report] LPSC17002, Laboratoire de Physique Subatomique et
This histogram, summing our data to a few num- ber of parameters and used along with Kullback-Leibler dis- tance, is shown to allow a rate of succesfull law recognition as good as
Concurrent infection with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus and Haemophilus parasuis in two types of porcine macrophages: apoptosis, production of ROS and formation
However, in 148PK15 P53−/− cells released from the G0/G1 phase, G1/S phase or G2/M phase synchro- nized cells, the cell population at the S phase in PCV2- infected cells
ICS‑assays revealed the presence of APP‑CCE specific CD4 + CD8α dim IL‑17A‑producing T cells in blood and lung tissue in most infected animals during the acute and chronic
Effects of infection and its interaction with housing on changes in antibody titers after infection After infection with PRRSV, there was no housing or infection effect on