Early lactation extended therapy against Staphylococcus aureus intramammary infections in heifers
Texte intégral
Figure


Documents relatifs
aureus strains are recovered from the cheeses (farms B, D, F, G,…..), they are always isolated from the nares of ewes in the flock (except for farm I).. That suggests that
Dear authors; three reviewers have provided comments and suggestions on various aspects of your study. Before a final recommendation by the PCI ANSC can be made, I invite
Hambraeus (1973) démontre avec une étude très élaborée dans un département pour grands brûlés, qu'une épidémie d'infections chez les patients est souvent
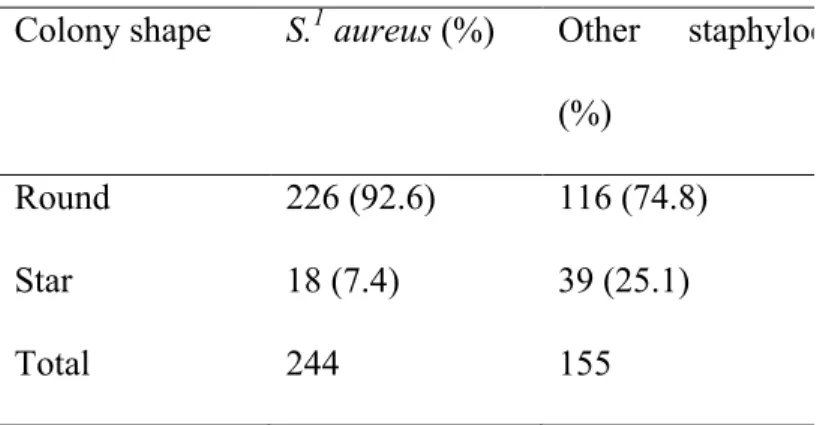
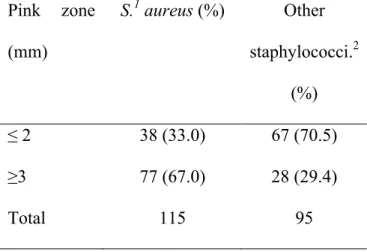
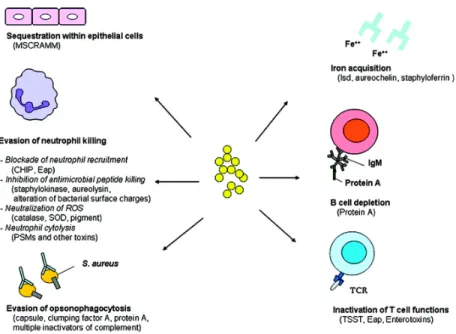
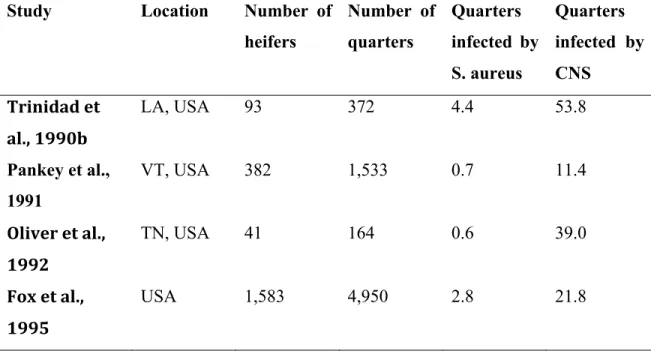
[r]
However, the distribution of the antibiotic MICs for the isolates from cured and persistent cases was different within the three study groups (i.e., extended therapies to
coli bacterial numbers for transient infec- tions after the initial acute phase will generally result in fadeout of the bacterial population and thus clearance of
RNA was isolated from the milk somatic cells of challenged animals and the expression of selected cytokine genes, including IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, TNF-α, IFN-γ, and GM-CSF,
Verbeke J, Piccart K, Piepers S, Van Poucke M, Peelman L, De Visscher A, De Vliegher S (2015) Somatic cell count and milk neutrophil viability of dairy heifers with specific