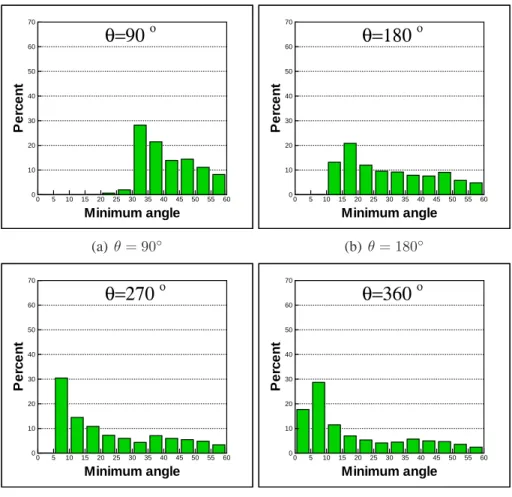
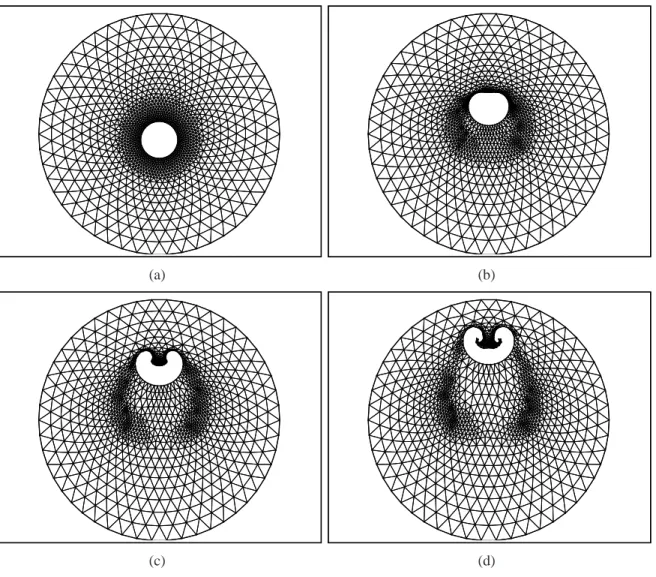
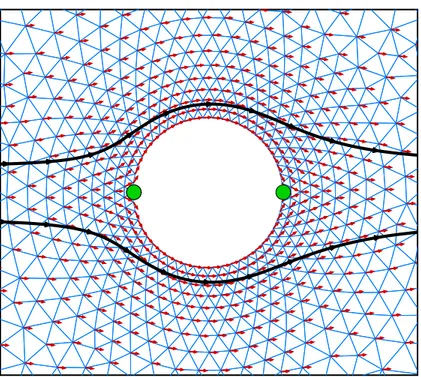
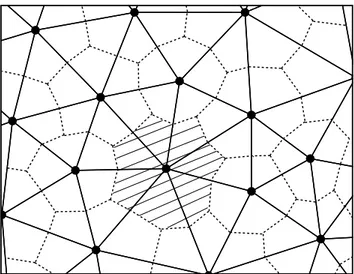
Unstructured Meshes for Large Rigid Body Motions Using Mapping Operators
Texte intégral
Figure



Documents relatifs
ﻟا ﺮﯿﺛﺄﺗ ﺖﺤﺗ داﻮﻤﻟا هﺬھ ﻲﻓ ﺔﺟوﺰﻠﻟا ﺮﺴﻛ كﻮﻠﺳ ﻰﻠﻋ ﻞﻣاﻮﻌﻟا ﺾﻌﺑ ﺮﯿﺛﺄﺗ ﺢﯿﺿﻮﺘﻟ ﻦﻣ اﺪﯿﺟ ﺎﻔﺻو ﺐﻠﻄﺘﯾ ﺖﻠﻔﺳﻹا كﻮﻠﺳ ﻞﯿﻠﺤﺗ .ﺔﻔﻠﺘﺨﻤﻟا طﻮﻐﻀ ﺟإ حﺮﺘﻘﻧ ﺎﻨﻧإ ،ﺔﺳارﺪﻟا
In Section 4, by relying on the viscosity property of the value function to its dynamic programming variational inequality, we give a first main result providing the structure of
Our approach effectively provides an optimized set of test models for both metamodels tested. In both cases, a specific configuration of parameters was found, which guarantees an
Motivated by recent work of Au, C´ ebron, Dahlqvist, Gabriel, and Male, we study regularity properties of the distribution of a sum of two selfad- joint random variables in a
The temperature of 350 K derived from Mariner measurements is considerably lower than the value found with the NPD data, but it is still significantly higher than the exospheric
They present a model with five delay differential equations (DDEs), three for the neutrophil dynamics (stem cell number, bone marrow and circulating neu- trophil count) and two for
In order to be able to analyse in TEM-STEM the crystallochemistry of recombining defects in p-type polysilicon (L = 100 pm), we have developed the scanning transmission
In this work, we have derived the incompressible Euler equations from the Boltz- mann equation in the case of the initial boundary value problem, for a class of boundary conditions