A bipolar consensus approach for group decision making problems
Texte intégral
Figure
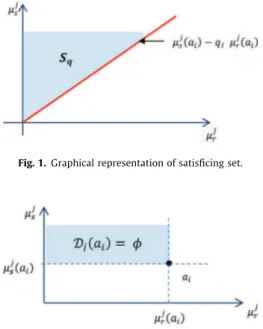
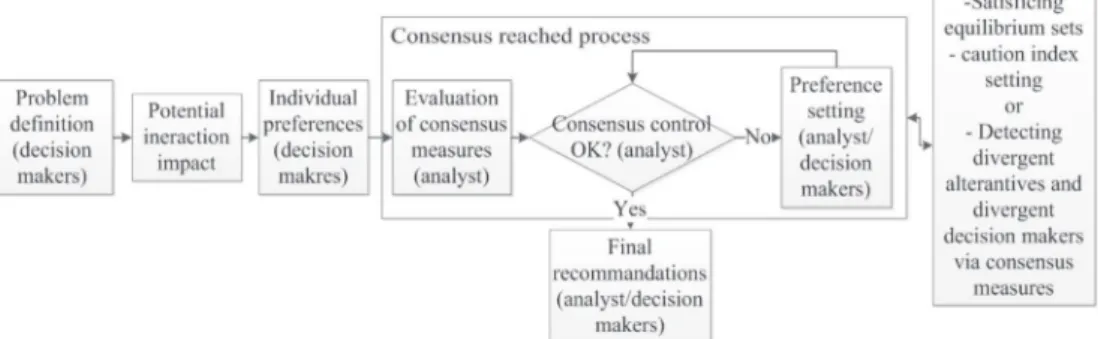

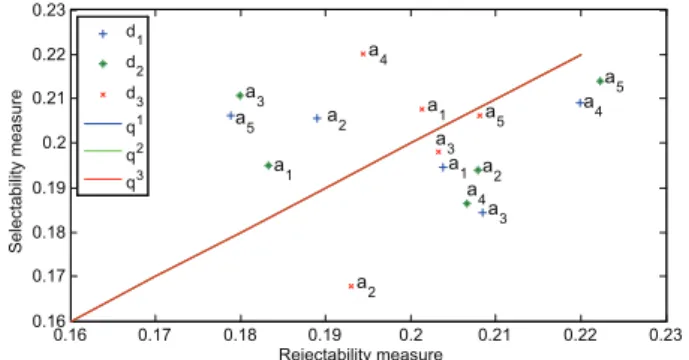
Documents relatifs
Finally, in chapter five, thanks to the use of stable water isotopes, it could be concluded that, even though fine tree roots were observed all through the soil profile
Pour que l’´ eclatement d’une vari´ et´ e diff´ erentiable en un point soit bien d´ efinie, il est n´ ecessaire que cette transformation soit invariante sous un changement
Alors, est-ce que vous pouvez nous dire un peu, pour qu’on comprenne bien, ce que 2.. vous vouliez dire à
Namely, we want to allow two kinds of decision making: first – users can like / dislike / discuss options (i.e. decisions); second – the software itself can also calculate an order
Alors, comme le juge Président vous l’a expliqué, je vais simplement vous poser 9.. quelques questions de
In Section 4 we sketch a purely algebraic proof of Theorem 1.2 (except for the explicit residue representation) based on Roos’ theorem.. In Section 5 we consider in some more detail
From the uniqueness result we deduce that any Coleff-Herrera current on a variety Z is a finite sum of products of residue currents with support on Z and holomorphic
This paper contains three sections : in the first one, different solution techniques for the set covering problem are described ; this section may be skipped, as it is