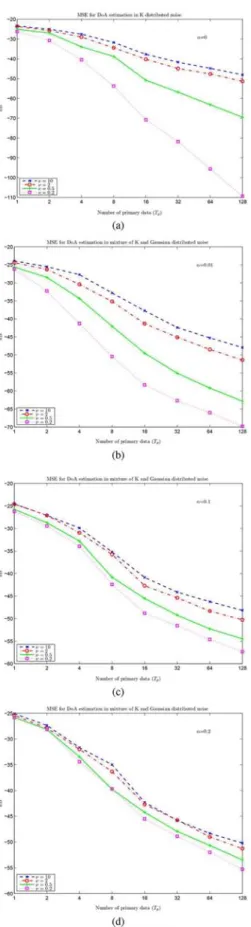
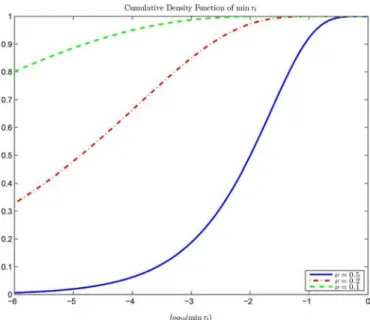
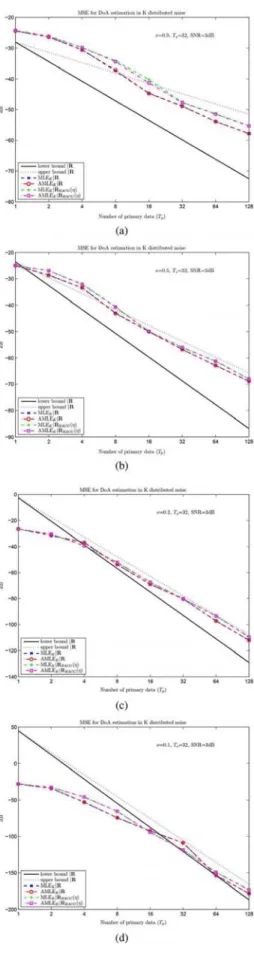
Bounds for maximum likelihood regular and non-regular DoA estimation in K-distributed noise
Texte intégral
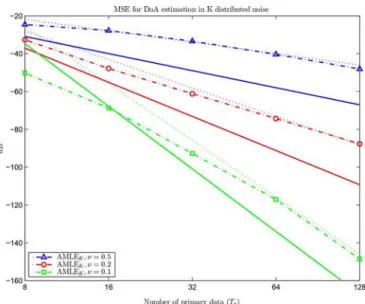
Figure
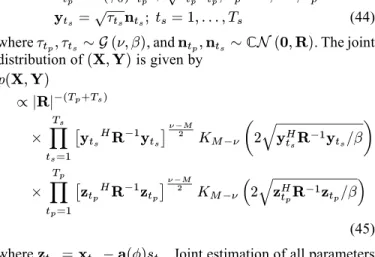
Documents relatifs
Indeed, within the context of estimation theory, with independent and identically distributed observations, the asymptotic efficiency and gaussianity of Maximum Likelihood (ML)
In this paper has been introduced a new MLE of the clutter subspace projector in the context of a low-rank SIRV plus white Gaussian noise which outperforms the classical estima-
Ainsi, dans plusieurs cas de construction de filières d’approvi- sionnement local pour la restauration collective et l’aide alimentaire, nous avons constaté qu’il peut être
Figure 5 illustrates the geometrical tracking principle using the 3D range information on the Lissajous pattern, to (a) identify targets on the object or any useful geometrical
As an example, to show the prediction of fire growth, smoke movement and occupant evacuation in this building, a non-flashover fire is assumed to have occurred in the centre
On the other hand, designers of adaptive frameworks can easily apply an existing indicator to an artifact specific to their learning situation (e.g., if an indicator has been
The documents may come from teaching and research institutions in France or abroad, or from public or private research centers.. L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est
S YSTEMIC OPTIMIZATION PROBLEM PROCEDURE In order to handle the optimization problem of the passive WT submitted to a consumption profile and a given wind speed, we have