A minimal model for hepatic fatty acid balance during fasting: Application to PPAR alpha-deficient mice
Texte intégral
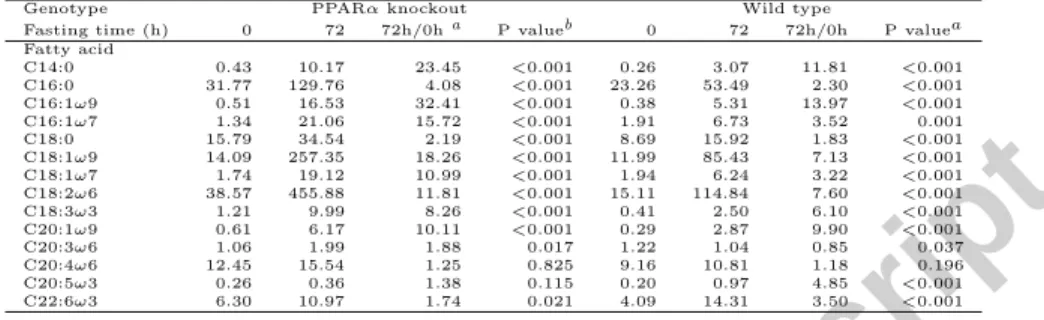
Figure



Documents relatifs
Behavior of the maximum leaf elongation rate (LER) ((a) and (b)) and of the leaf blade length ((c) and (d)) on the main stem through increasing leaf rank and the interaction
emergence, time to flowering) and elongation rate (of different leaves, of different internodes) are related to temperature with the same parameters. – these parameters are stable
Relationship between position of the leaf and duration of the exponential elongation phase a, duration of the linear phase b for leaves 5 to 22 and final blade length c for leaves 1
(A-E) Expression levels of the FOXA2 target gene Igfbp1, of the FXR target gene Slc51b/Ostb and of the gluconeogenic genes Fbp1, Pck1 and G6pc in response to GW4064, insulin,
Capitaux permanents Immobilisations Dettes à court Et Moyen terme Stocks Créances clients Y compris effets TRESORERIE Emplois Ressources ACTIF PASSIF...
Caspase-3 immunolabelling was quantified on entire tumor slices, and revealed that sunitinib and sorafenib significantly increased apoptosis after 14 days of treatment (D28) (G),
Taken together, these results demonstrated that the secretion of TG containing fatty acids produced de novo by chicken hepatocytes is highly dependent on the level of
Here, we show that IGF-I may be involved in axon elongation in a specific subpopulation of hypothalamus neurons. Indeed, the present study indicates that i) IGF-I preferentially




