Enhanced error estimator based on a nearly equilibrated moving least squares recovery technique for FEM and XFEM
Texte intégral
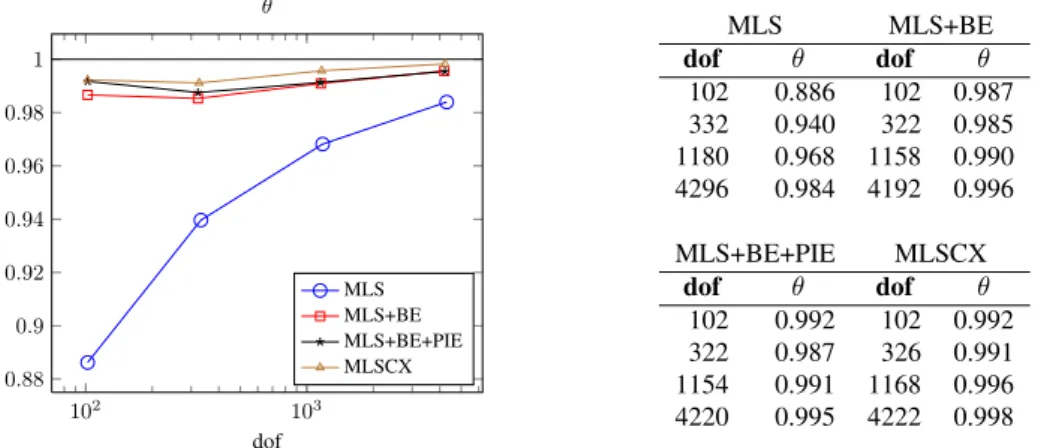
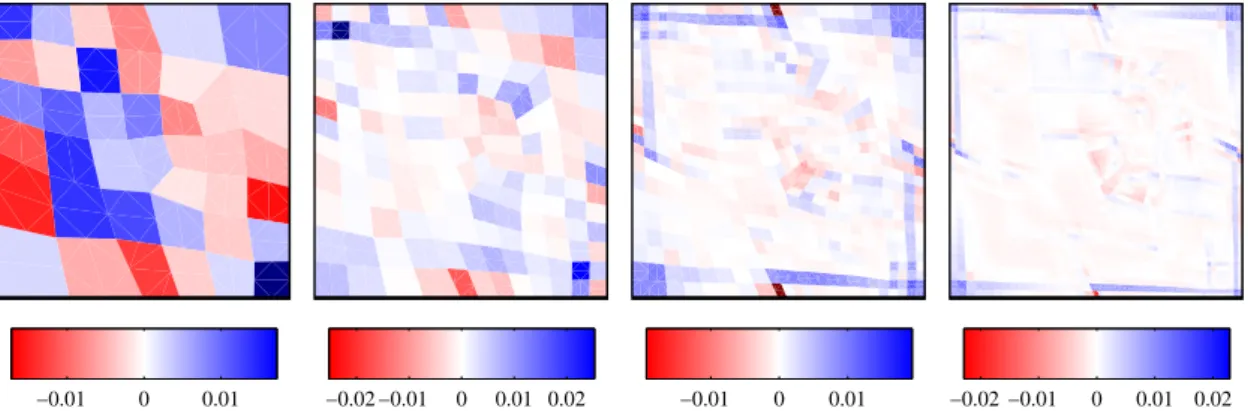
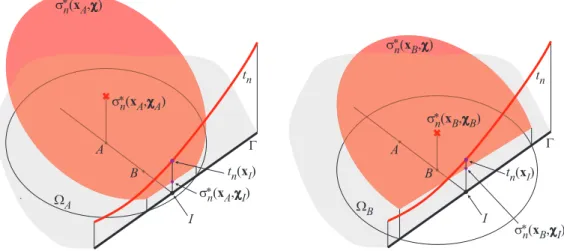
Figure


Documents relatifs
The CGAL 3D periodic triangulation package [8] currently allows to handle Delaunay triangulations in the 3D flat torus R 3 /(Z 3 , +), for which the group is generated by three
Here, we present an error estimation technique for enriched finite element approxi- mations that is based on an equilibrated recovery technique, which considers the stress
This note deals with the approximation of distributed null controls for the Stokes equation. The existence of L 2 controls have been obtained in [Fursikov &
modified d e sign, Experience with the operation of snow-melting systems in England (14) has indicated that traffic removes snow and slush when only 60 per cent
Formulation of LS Estimator in Co-Array Scenario In this section, as an alternative to co-array-based MUSIC, we derive the LS estimates of source DOAs based on the co-array model
A posteriori implicit residual-type estimators have traditionally been the most commonly used tech- niques to provide bounds of the error of the finite element method,
This paper introduces an error estimator based on the constitutive relation which provides an upper bound of the global error for parametric linear elastic models computed with
KEY WORDS : finite element method; equilibrated stress recovery; constitutive relation error; error bounds; goal-oriented error