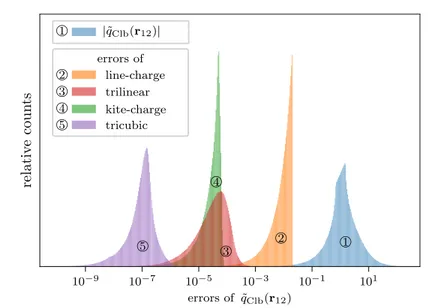
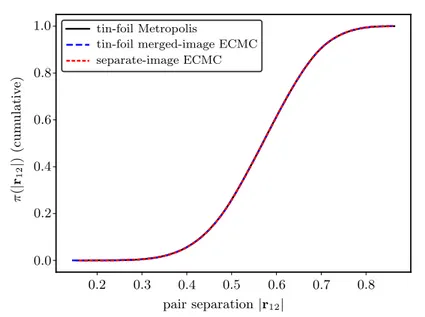
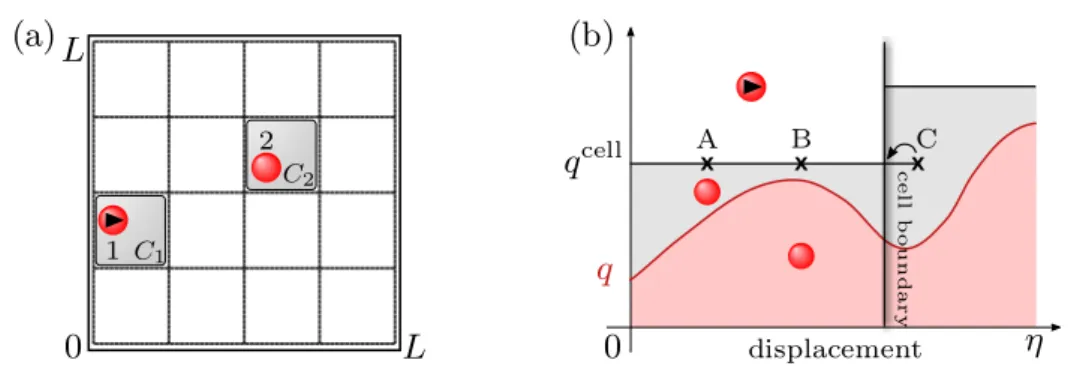
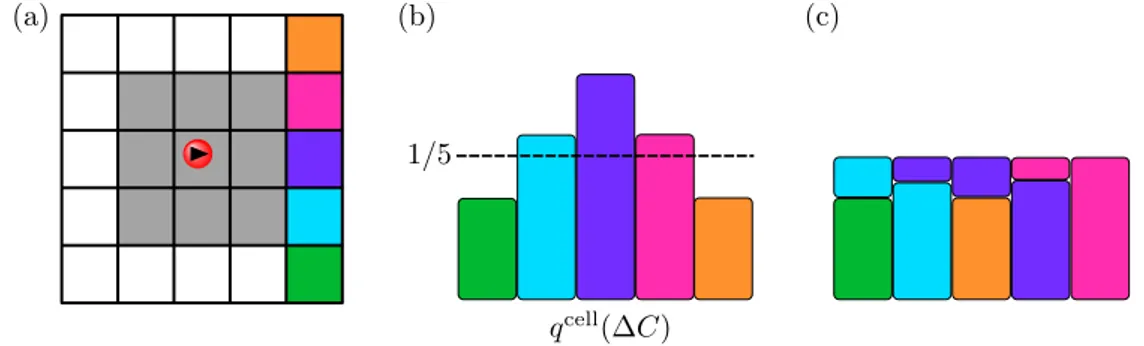
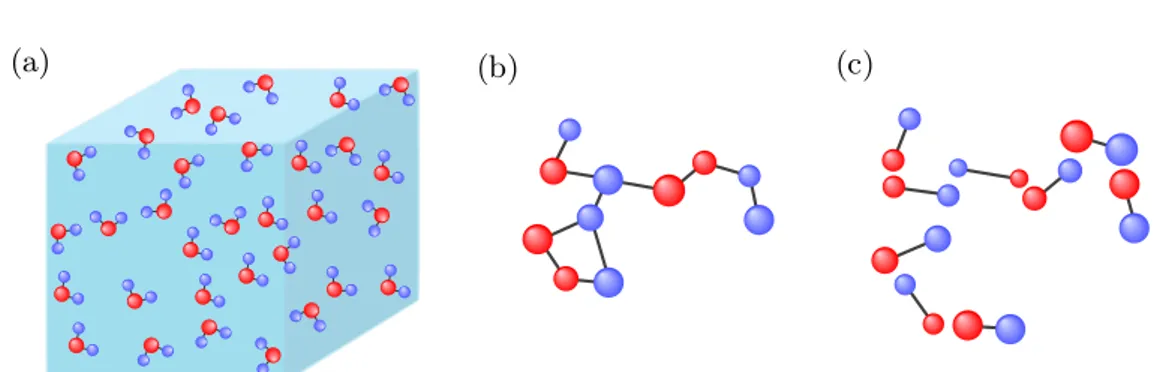
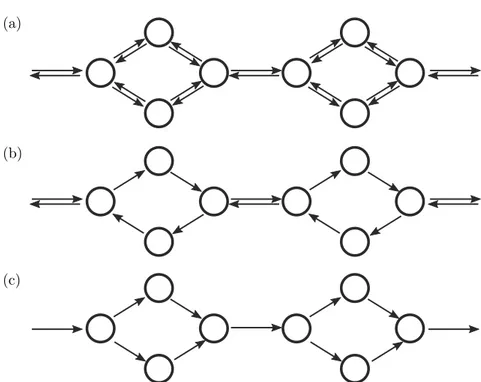
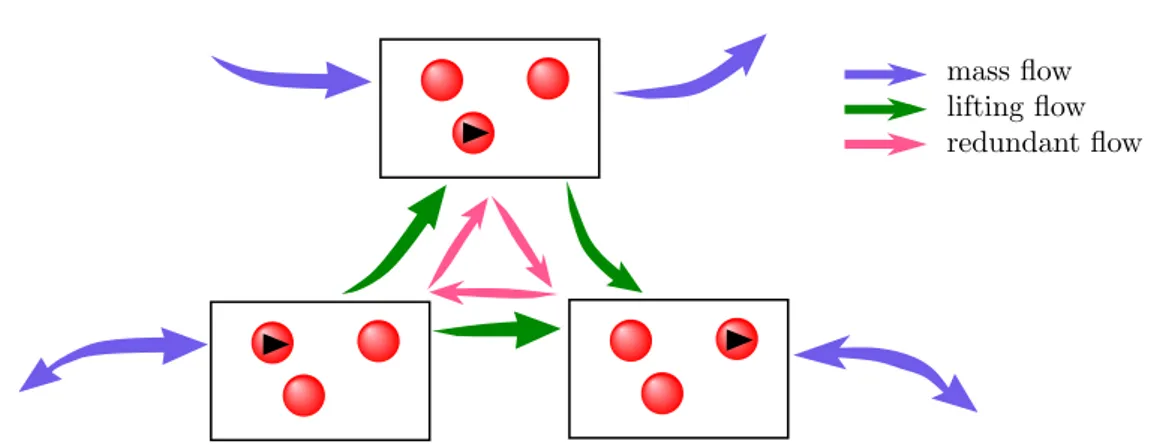
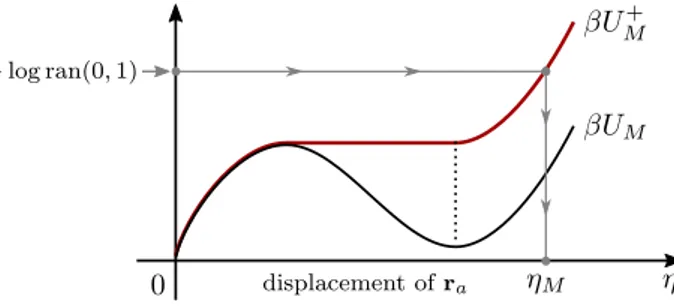
Application of irreversible Monte Carlo in long-range realistic systems
Texte intégral
Figure

Documents relatifs
Positive kSZ radial profile (blue) around the 14 093 WHL clusters with the Planck temperature map at 217 GHz with the 1σ uncertainty estimated by a bootstrap resampling, and
In the long term, however, there is no significant difference between treatment and control groups in terms of the average time each user views each ad, but there is
Ces données sont en accord avec celles obtenues in vivo, puisque la micro- injection de morphine dans la VTA n’induit plus d’augmentation de l’activité électrique des
Abstract To determine the prevalence of Chlamydophila psittaci in wild birds, cloacal swabs from 527 songbirds, 442 waterfowl, 84 feral pigeons, and 38 cormorants were examined
These were generated by binning the initial phase space parameters θ, φ, δ into 20000 vec- tors each corresponding to a trajectory defined by unique (θ, φ, δ) values. These vectors
un modkle qui tient compte de l'interaction A courte distance seulement. En consequence, on decrit habituellement les transitions de Mott ou de Peierls comme des transitions du
This method uses spherical near-field (NF) data to determine an equivalent set of tangential infinitesimal dipoles that reproduce accurately the antenna radiation field, both
2014 The influence of permanent dipoles on the nematic isotropic transition is studied by adding a simple polar interaction to the Maier-Saupe model of nematic