Systematic design of tetra-petals auxetic structures with stiffness constraint
Texte intégral
Figure
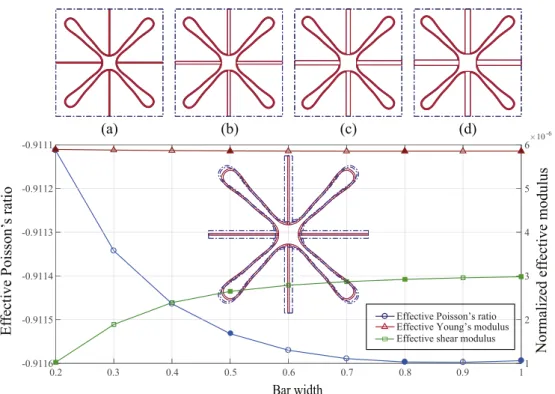
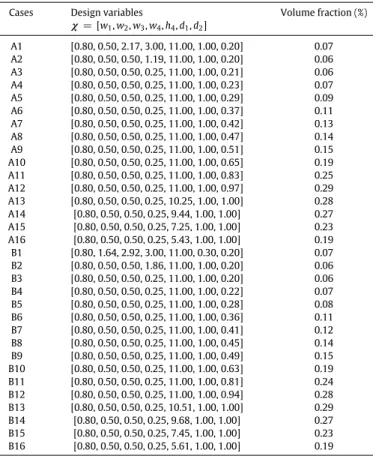
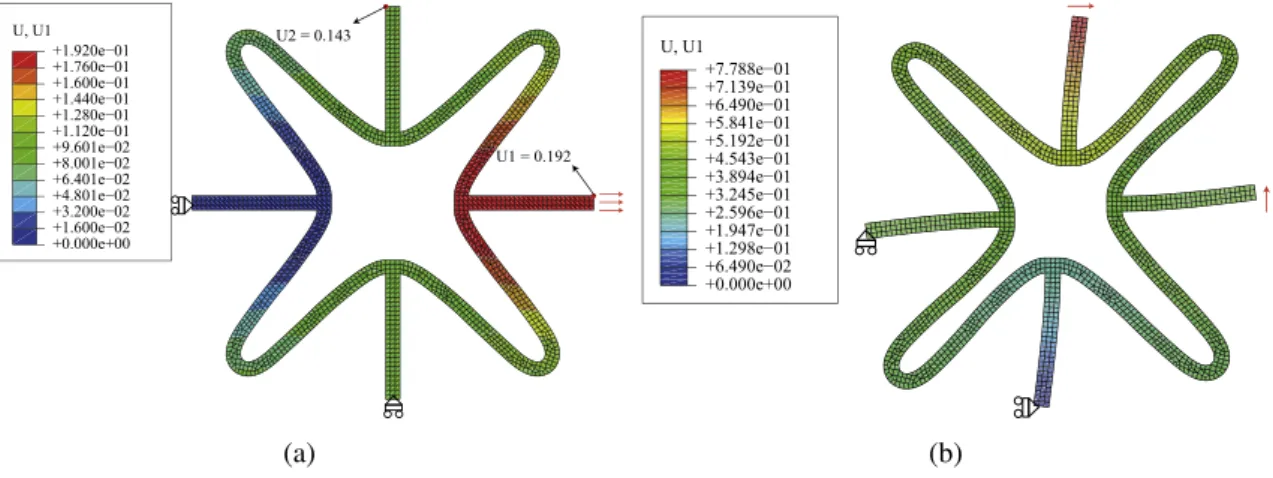
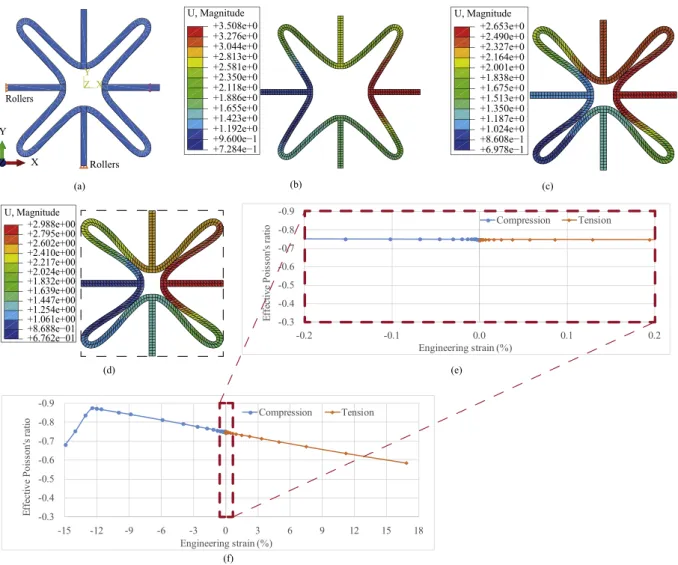
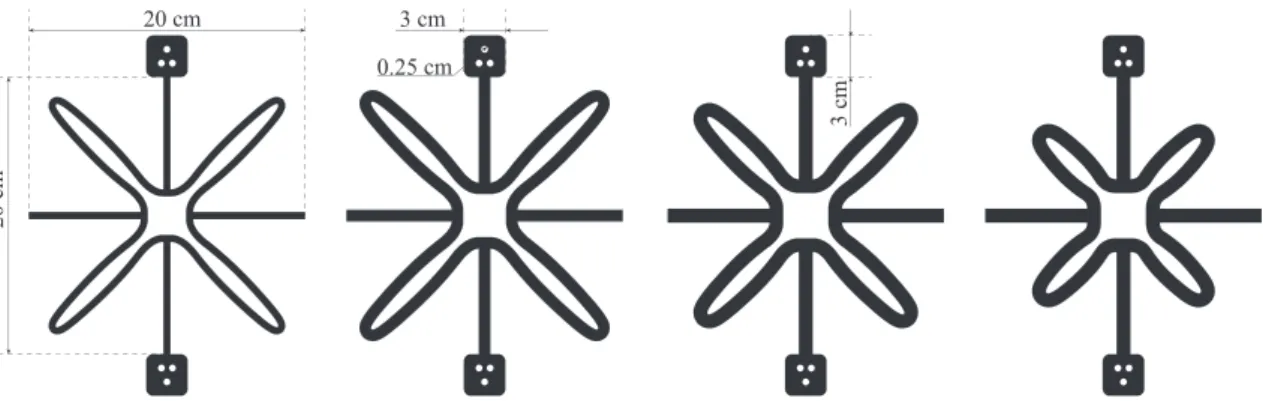
![Fig. 1. (a) Star-shaped auxetics and the mechanism at the vertices. The study in Ref. [1] focuses on (b) the design of exterior petal boundary subjected to a geometric width constraint, while the study in this work focus on (c) the optimal shape form and p](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/7429201.219685/3.892.149.736.89.255/auxetics-mechanism-vertices-exterior-boundary-subjected-geometric-constraint.webp)



Documents relatifs
Tool is also user friendly provides rich amount of the information about the distributed application like active objects, threads, requests, connections between the
The fifth plenary meeting of the COST E21 Action was hosted by Dr Radoglou (NAGREF) in Thessaloniki (Greece) 27–29th November 2003, where 22 oral communications and 36 posters
In the later works the group of Maxim Bazhenov included intracellular sodium accumulation into the model of spike-and-wave discharges (Krishnan and Bazhenov
The Application Heart- beat framework was used to provide the necessary sensors to develop different solutions, spanning from machine learning techniques to heuristic
To further characterize the ligand binding mode, we used Microscale Thermophoresis to determine the affinity of ENDO-WT and mutants ENDO-D88A and ENDO-D118A for DPBA (1) and
Currently, there are three conventional tests to diagnose Chagas in its chronic phase: IHA, IIF and
Paleoproterozoic spherule layers from Greenland (Grænsesø) and Russia (Zaonega), as well as some distal ejecta deposits (Lake Superior region) from the Sudbury impact
We tested a panel of guides targeting the β-catenin transcript (CTNNB1) at known phosphorylation residues and observed editing levels between 5% and 28% (Fig. 2C), resulting in