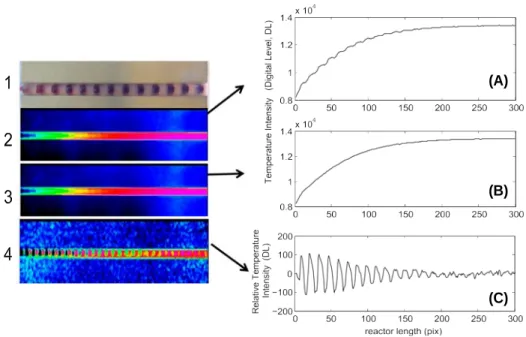
Quantitative thermal analysis of heat transfer in liquid–liquid biphasic millifluidic droplet flows
Texte intégral
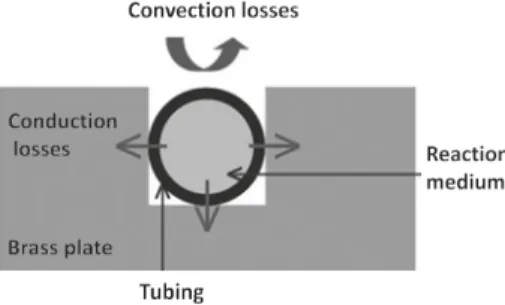
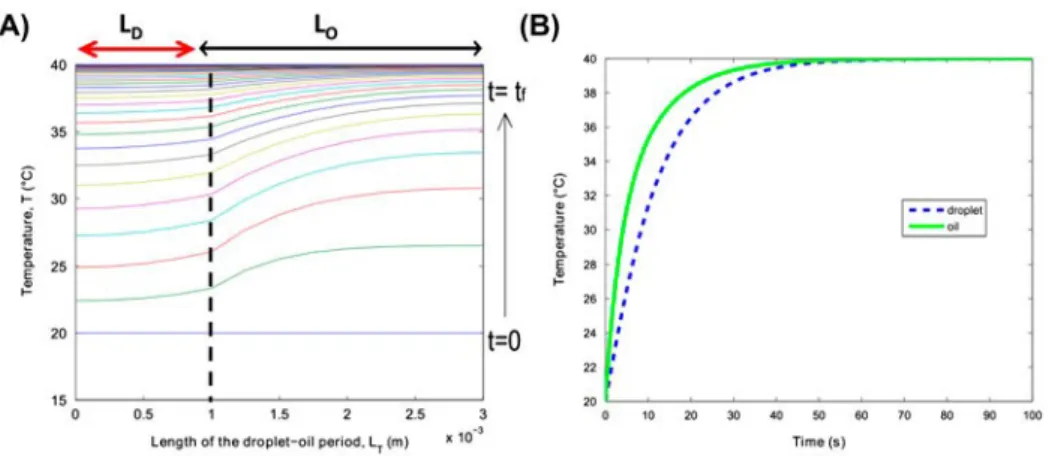
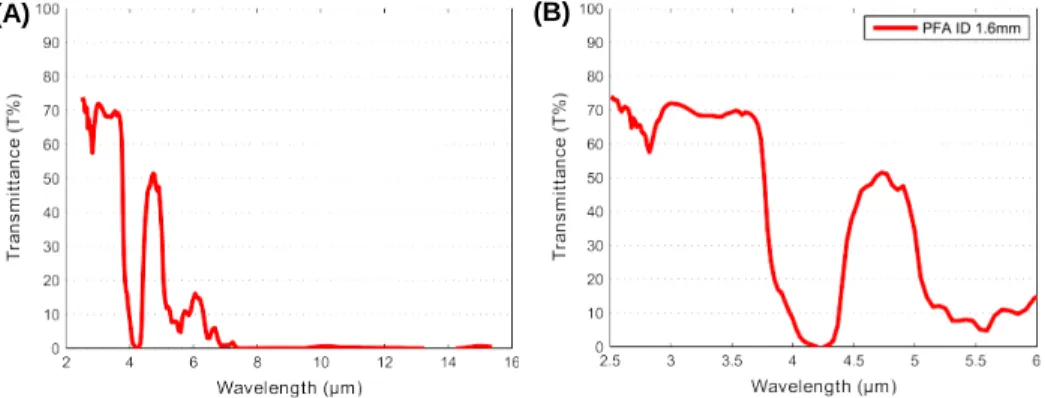
Figure


Documents relatifs
Here we use another way of describing the nematic phase by making the good approximation that the degree of order versus reduced temperature is an universal
Spectra of velocity fluctuations, liquid volume fractions, and vapor scalars for interfacial flows with strong deformations of the interface (including high density ratios) have
They allow a better understanding of the physical mechanisms involved in the non- Newtonian temperature dependent fluid flows: with increasing P n, the relative viscosity is
Key words and phrases: Heat transfer; Thin liquid film; Asymptotic modelling; Long waves; Thermal dependency properties; Marangoni effect.. MSC: [2010]76D33 (primary), 76B25,
In acetonitrile, it is shown that when 2 nitrate ions complex to uranyl, they are in the bidentate mode and that the total coordination sphere of uranyl comprises
Cost analysis and industrial viability In 2008 was published [7] a cost assessment of standard technology based on mc-Si solar cells with 15% solar cell efficiency in the range of
We first characterize the single-phase flow, in terms of threshold for transition to turbulence, scaling of the torque and measurements of the mean flow and of the Reynolds stress
As the mechanism of their formation was not clarified, this studywas carried out to know the state of electron aroundiron species in the aluminous oxide by means of M6ssbauer