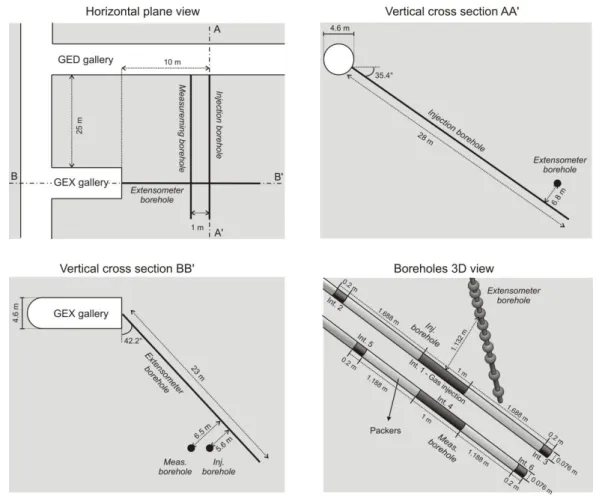
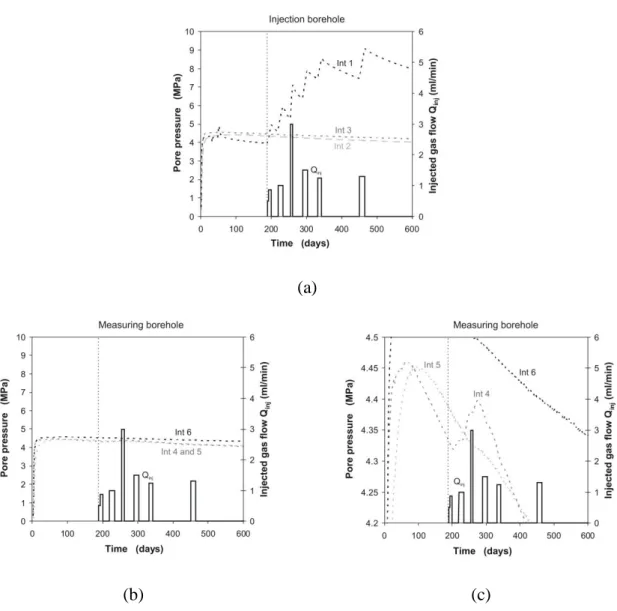
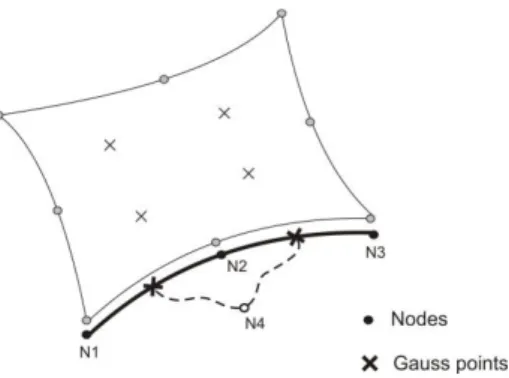
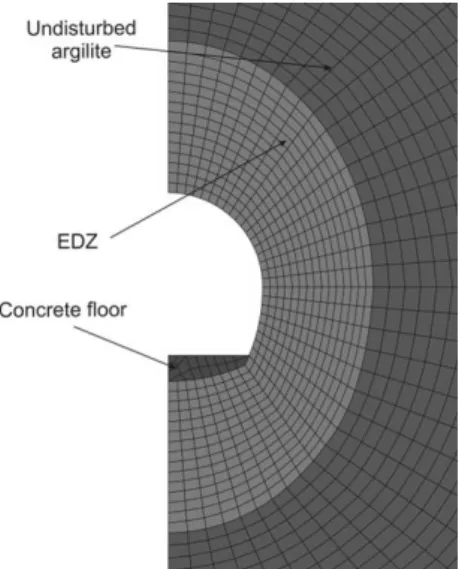
An unsaturated hydro-mechanical modelling of two in-situ experiments in Callovo-Oxfordian argillite
Texte intégral
Figure
Documents relatifs
L’accès à ce site Web et l’utilisation de son contenu sont assujettis aux conditions présentées dans le site LISEZ CES CONDITIONS ATTENTIVEMENT AVANT D’UTILISER CE SITE
Moreover, in order to identify the main chemical reactions during cement paste carbonation, simulations on reactive transport were performed by BRGM using TOUGHREACT, a
Thermodynamics of chemical reactivity in capillary systems The chemical behavior of capillary systems has been studied for more than ten years, and the theoretical framework is now
Interestingly, α7Β integrin levels were significantly increased after L-Arg treatment in cardiac muscle and diaphragm from 5-week-old mdx mice compared to 5-week-old Ss-treated mdx
The voltage- sensor trapping model of β-scorpion toxin action (48) implies that the toxin initially binds to the resting state of the channel and subsequently binds
Flow cytometry analysis ( Figures S1 B and S1B’) of immune cells showed that in both models, the main cell type pre- sent in dystrophic fibrotic muscle was macrophages, which
L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, émanant des
For the least square estimator (LSE) we do the following: we estimate the parameter σ explicitly from the observations of the second variable by (23), and then compute the parameters