Average-case complexity of a branch-and-bound algorithm for maximum independent set, under the $\mathcal{G}(n,p)$ random model
Texte intégral
Figure
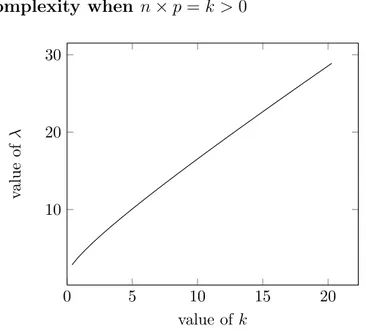
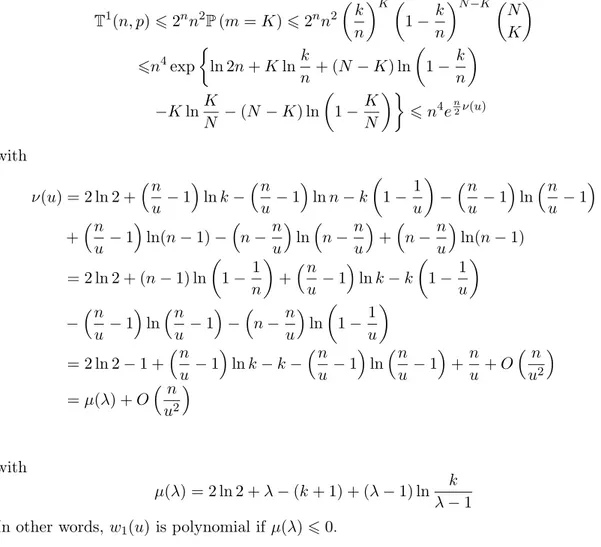

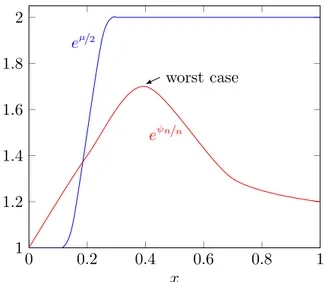
Documents relatifs
Table 4 reports the size of the critical tree for five branching rules (two static rules Forward, Alternate, and three dynamic strategies MaxSum, MinMin and MinBranch) and two
We present current noise measurements in a long diffusive superconductor - normal metal - su- perconductor junction in the low voltage regime, in which transport can be
It is known that a maximum independent set of a graph on n vertices can be computed in O(1.4423 n ) time by combining a result due to Moon and Moser, who showed in 1965 that the
We consider the solution of hard problems of the knapsack family, like multidimensional knapsack problems or knap- sack sharing problems, to become possible in reasonable time with
As of 2014, the state-of-the-art method for solving problem (1) to optimality is the semidefinite-based branch-and-bound algorithm of [MR12] which is able to solve instances of size n
The parameters studied included bad level, amount of steel reinforcement, effective length of column, concrete strength, moisture Content, area and shape of cross
For every p-pass Shellsort algorithm and every increment sequence, every subset of n!/2 n input permutations of n keys contains an input permutation that uses ⍀ ( pn 1⫹(1⫺⑀)/p