Localization Precise in Urban Area
Texte intégral
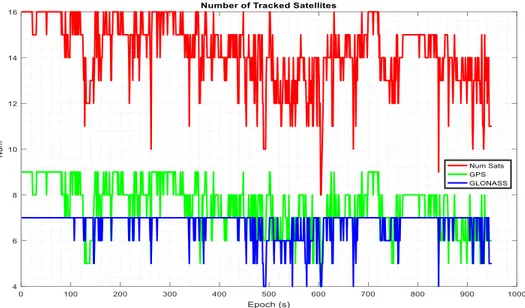
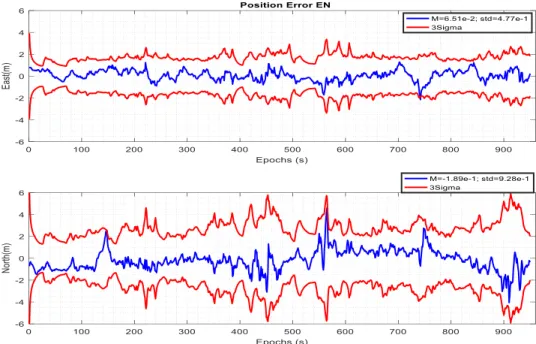
Figure
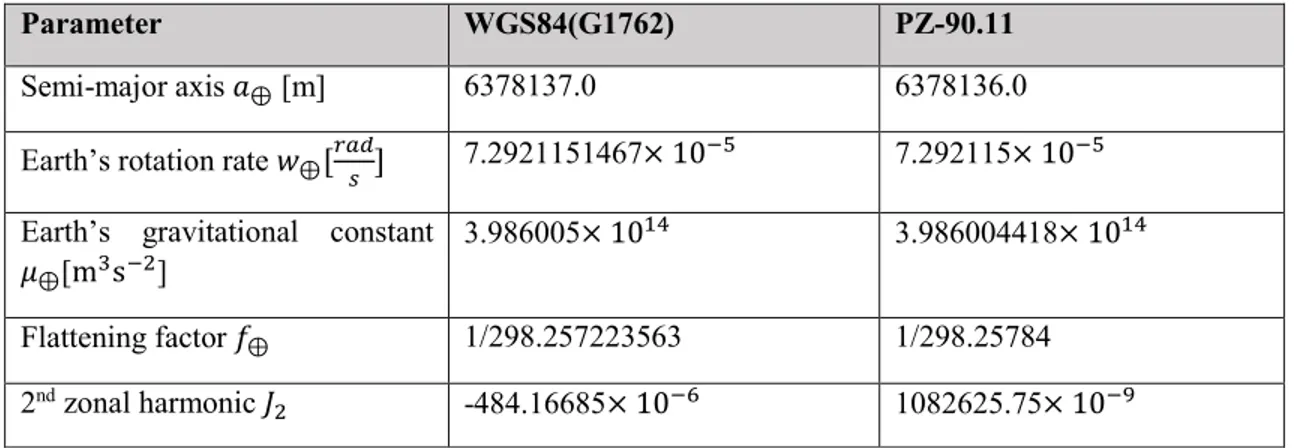
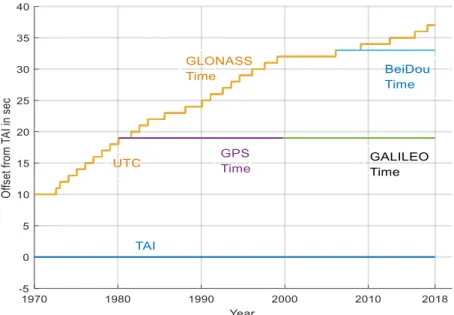
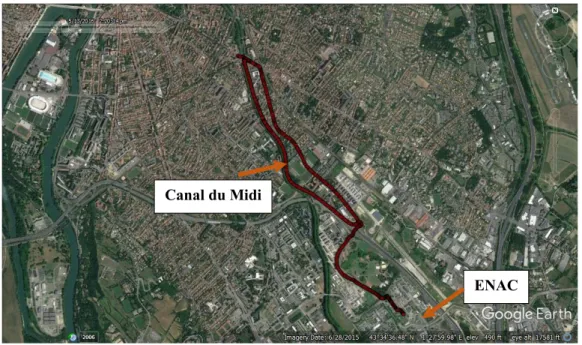

Documents relatifs
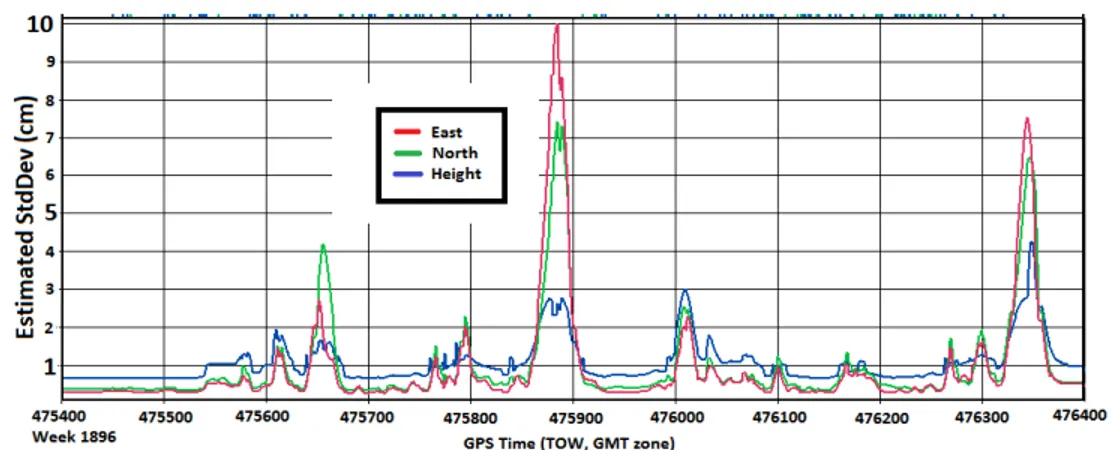
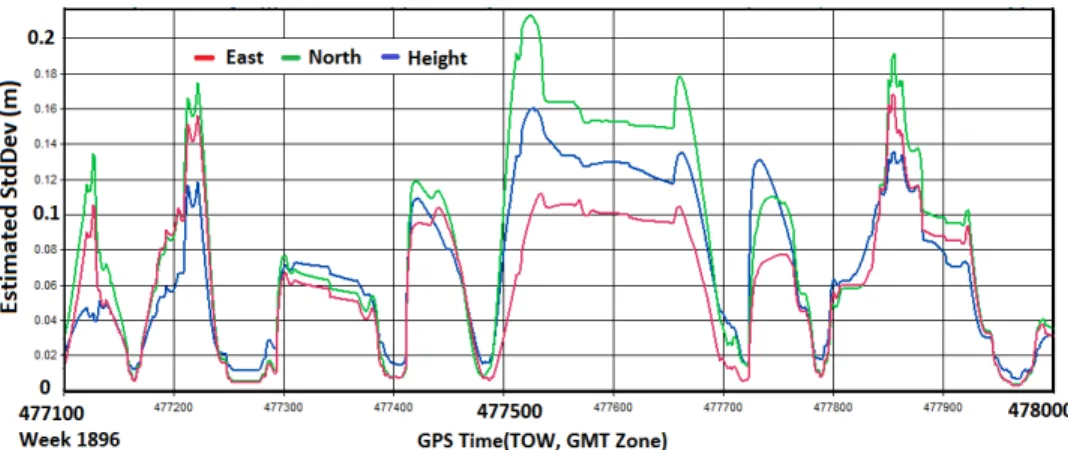
However, the estimation of ambiguity as a constant thanks to the cycle slip resolution technique, as well as the appropriate weighting of measurements and the
In this paper, a new approach to localization integrity for land mobile robots is proposed by combining vehicle and GNSS data, stored within a short-term memory, the data horizon..
The robust pose estimation consists in computing the vehicle’s position and heading at time t, given a finite number of prior position measurements and inputs, under the hypothesis
With the purpose to develop a safe path planning with obstacle avoidance capabilities, a model predictive control approach is developed, which uses the environment information
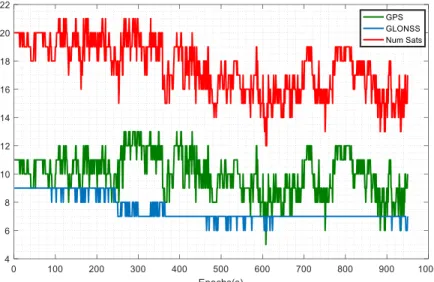
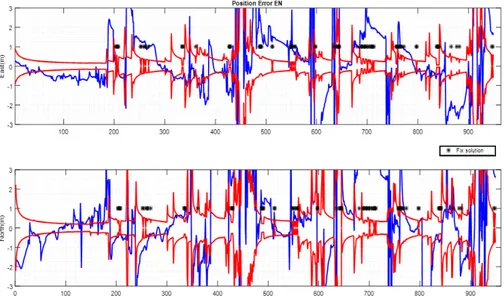
For each segment in the road cache, a tightly coupled positioning solution is computed using the unknown elimination method described pre- viously in Sec.3.4 in order to determine
We limit ourselves to clustering algorithms which try to minimize the sum of the intra-cluster distances or approximate the minimum and such that the cardinality of each cluster is
Despite a human-like behaviour of the automated system, robustness and usability are limited (Barto, 2019). A control algorithm for combined position and force control for
The OBIWAN algorithm presented in this paper reduces the contribution of the reference receiver to the initial float solution in terms of noise and multipath,