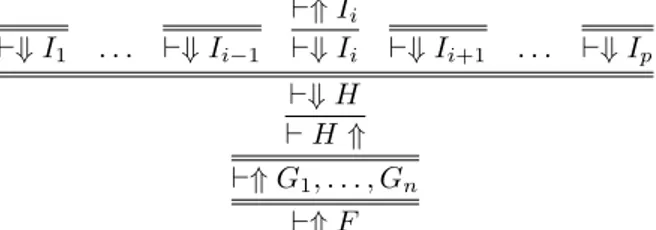Symmetric dialogue games in the proof theory of linear logic
Texte intégral
Figure




Documents relatifs
A set of threads S is winning when it is non empty, stable under extension by mandatory moves, and when every thread in S ending on a positive sequent has an extension by a proper
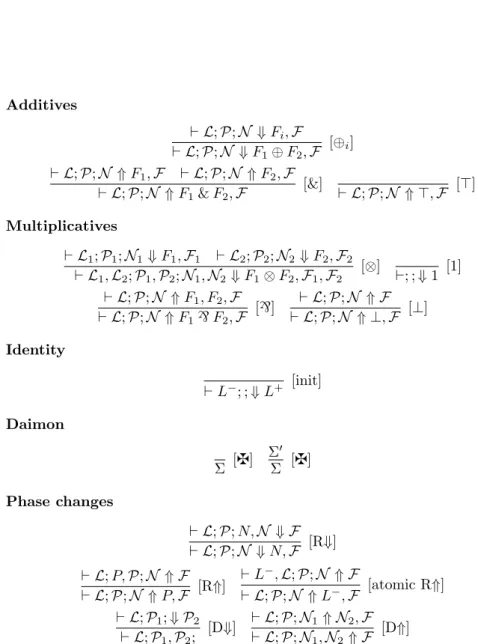
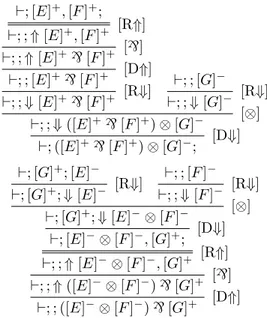
In this paper, we propose a simple interpretation of the most standard focused presentation of MELL, showing how the structure of focused proofs can be described by refined
For example, intuitionistic logic was developed to rid (classical) logic of certain logical principles and model checking
This model is interesting in the following respect: while it is obvious that the objects interpreting formulas are games and that everything is developed with the intuition
Due to the presence of the self-dual non-commutative operator from BV, the calculus MAV is defined in the calculus of structures — a generalisation of the sequent calculus
In our model, logic programs are embedded in logic units named Logic Fragments. The following set of definitions will be used to clarify the concept. We assume that P rop, Const and
A regular behaviour is such that its set of visitable paths is exactly the set of positive-ended chronicles of its incarnation, stable by shuffle and dual operations, where a shuffle
Based on this result, models based on deterministic graph- ings – or equivalently on partial measured dynamical systems – can be defined based on realisability techniques using