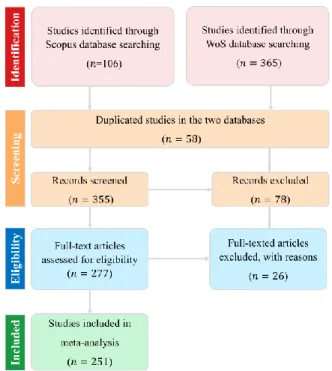
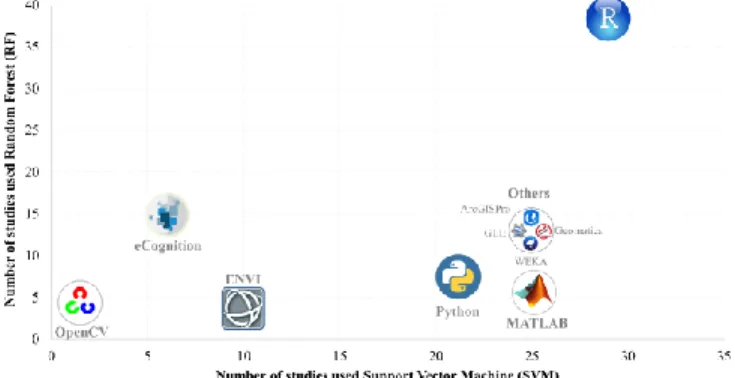
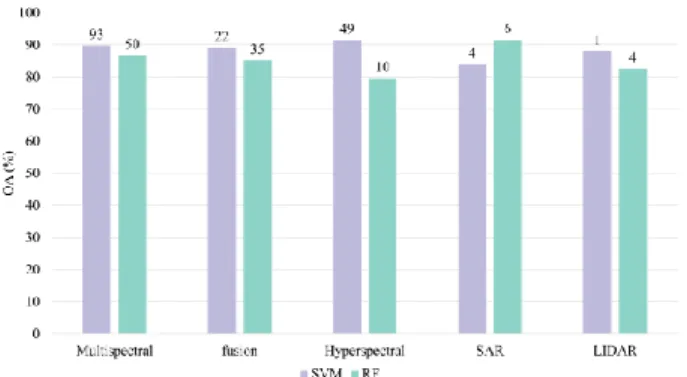
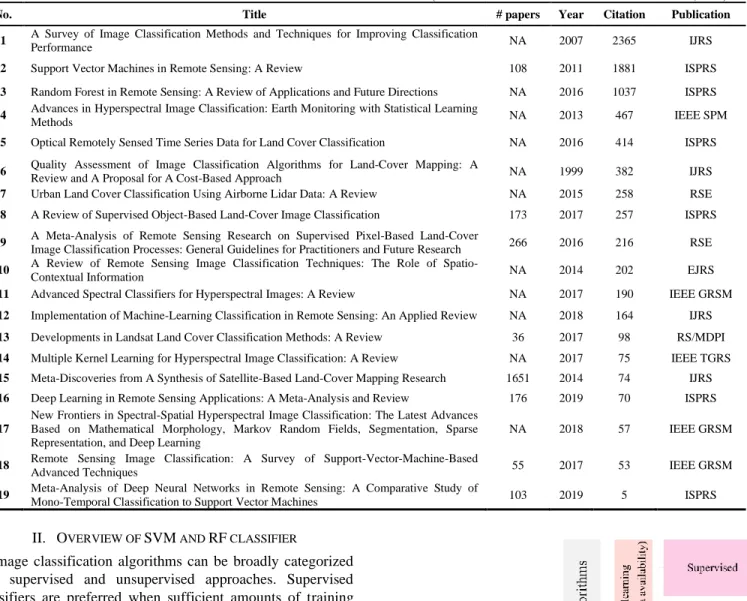
Support Vector Machine Versus Random Forest for Remote Sensing Image Classification: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review.
Texte intégral
Figure

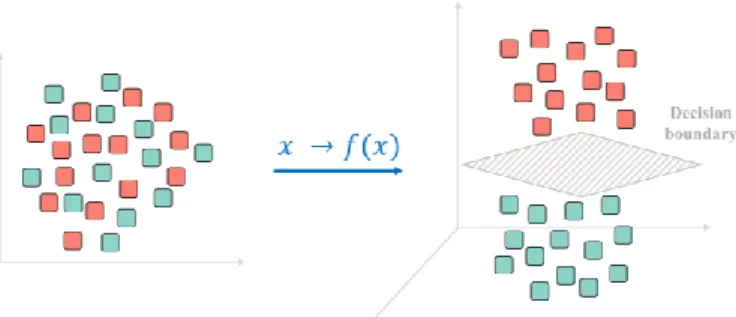

Documents relatifs
definition of vulnerability we use, they cannot logically modify the associations between heat and mortality... In addition, the reference sections of studies identified as
Specifically, we calcu- lated unadjusted repeatability (R), repeatability adjusted for test order (R n ), and repeatability adjusted for test order and individ- ual determinants (R ni
Studies show that adverse changes in retinal vascular caliber (principally narrower retinal arteriolar caliber and wider venular caliber) are associated with cardiovascular
Quinolones versus macrolides in the treatment of legionellosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.. Charles Burdet, Raphaël Lepeule, Xavier Duval, Marion Caseris, Christophe
Study Location Period Study Design Congenital Categories Exposure Assessment Exposure Variable Air Pollutants Results Confounders.. Gianicolo
Dans les entreprises de 10 salariés ou plus de l’ensemble de l’économie hors agriculture et hors emplois publics, 84,3 % des salariés travaillent à temps complet au
Lanham-New 1 1 Nutritional Sciences Division, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, University of Surrey, Guildford GU2 7XH, 2 Centre for Health Economics, University of York,
The second part is a meta-analysis of the effectiveness of gamification (assessed through RCT studies) applied to cognitive training with the following objectives: (1) assess