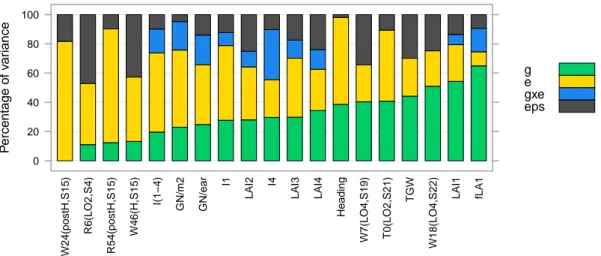
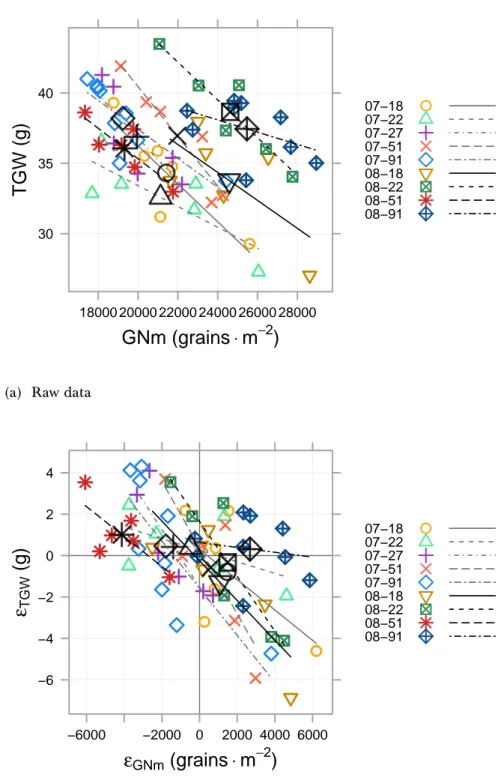
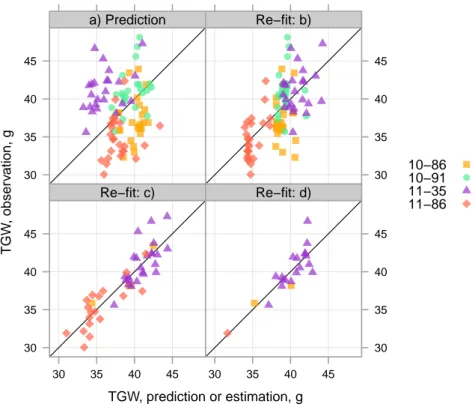
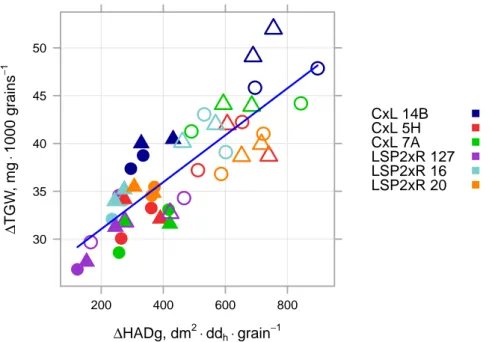
The tolerance of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to Septoria tritici blotch
Texte intégral
Figure
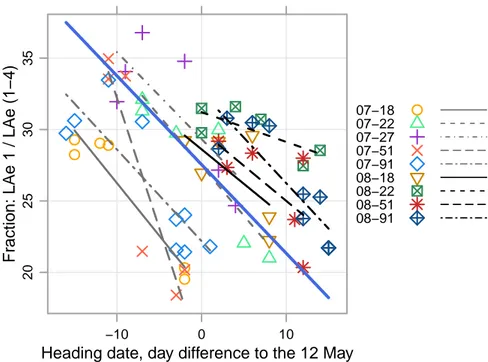
Documents relatifs
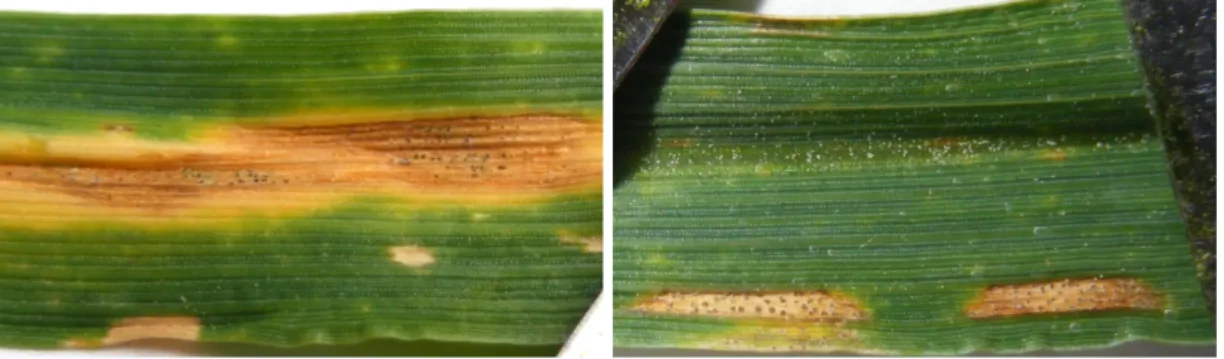
Septoria tritici blotch caused by the fungal pathogen Mycosphaerella graminicola is currently one of the most frequently reported diseases on both bread wheat and durum wheat in
high level of outcrossing has also been observed in a recurrent selection pro- gramme based on the same genetic background as the PA populations. Spikes or spikelets
mean rates of grain growth in apical and basal ears parts in Apache and in central and basal parts in Renan, even though the initial grain weights were not significantly
Several genes involved in resistance signaling were specific- ally repressed in JaloEEP558 such as the homolog of PATHOGENESIS-RELATED 1 (PR1, Phvul.006G197100) that was
L’accès à ce site Web et l’utilisation de son contenu sont assujettis aux conditions présentées dans le site LISEZ CES CONDITIONS ATTENTIVEMENT AVANT D’UTILISER CE SITE WEB.
Highly concentrated pollution plumes em- anating from the Mexico City urban agglomeration revealed that mixing ratios of Hg ◦ as large as 500 ppqv were related to combustion
L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, émanant des
Marti, “ Empirical rheology and pasting properties of soft-textured durum wheat (Triticum turgidum ssp. durum) and hard-textured common wheat (T. aestivum) ,” Journal of Cereal