Monotone combined finite volume-finite element scheme for a bone healing model
Texte intégral
Figure


Documents relatifs
The aim of our work is to design and study a coupled nu- merical scheme for poroelastic problems using this virtual element method formulation for the mechanical equilibrium
We propose in this paper a finite-volume scheme to approximate these measures. We show, thanks to the proof of the tightness of the approximate solution, that the conservation of
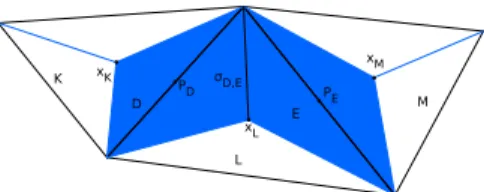
Key words: degenerate parabolic problem, convection–diffusion–reaction equation, inhomoge- neous and anisotropic diffusion, convection dominance, nonmatching grids, finite
Wellknown discretization methods are finite differences, finite volumes and finite elements. The mathemat- ical study of convergence is quite wellknown in the case of
Second, the numerical fluxes defined for the finite volume computation of the temperature are e ffi ciently derived from the discrete finite element velocity field obtained by
Firstly, the stabilization term T stab,2 is used in two of our proofs: first to ensure the convergence of the discretization of the mass convection flux div(ρu) and, second, for
Ce texte présente plusieurs énoncés qui assurent l’existence d’un vecteur non nul de petite hauteur dans un espace vectoriel de dimension finie sur un corps de nombres et qui évite
Additionally, the errors due to the averaging function should be characterized as a function of wavelength and intensity. We do not have enough experimental data