The Renaming Problem in Shared Memory Systems: an Introduction
Texte intégral
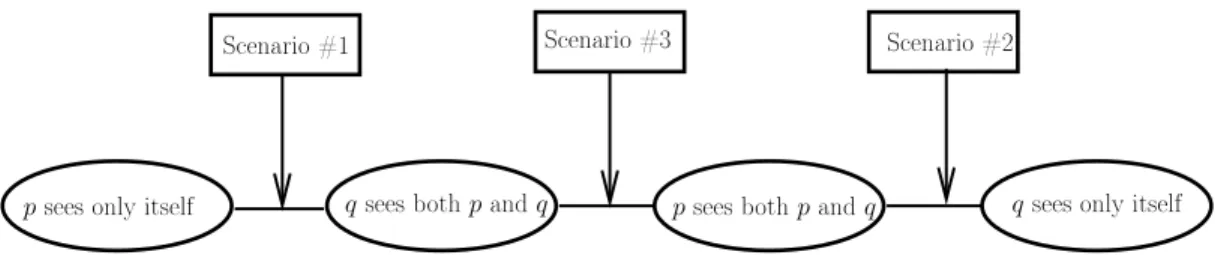
Figure
![Figure 3: A wait-free implementation of a splitter object (code for p i ) [38, 42]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/11330810.283450/8.918.341.575.900.1049/figure-wait-free-implementation-splitter-object-code-p.webp)
![Figure 4: A simple read/write wait-free adaptive (2p − 1) -renaming (code for p i ) [10]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/11330810.283450/9.918.192.718.732.962/figure-simple-read-write-wait-free-adaptive-renaming.webp)
![Figure 5: Recursive adaptive renaming algorithm (code for p i ) [48]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/11330810.283450/11.918.274.649.423.616/figure-recursive-adaptive-renaming-algorithm-code-p-i.webp)
Documents relatifs
Given that there is a unique solution for the GAP, it is still im- possible to develop a correct message passing algorithm which can terminate in pseudo-polynomial number of
Actually, the main idea behind the snap-stabilization is the following: the protocol is seen as a function and the function ensures two properties despites the arbitrary
We also prove that the class of generators of L ∞ -type pseudo-resolvents generalizes the class of infinitesimal generators of C o -equicontinuous semi- groups acting on
The dynamics of reaction time on performing the probe-task in parallel solution of the main thinking problem (insight / algorithmic) in provisional experimental
If activating one of the blue robots, it does not reach the position occupied by the red one, activate all blue robots If activating the red robot, it does not reach the position
It is possible to design an adversary that lets the robots occupy two distinct positions on the plane in a finite number of cycles….. MulHplicity DetecHon
Unite´ de recherche INRIA Rennes, Irisa, Campus universitaire de Beaulieu, 35042 RENNES Cedex Unite´ de recherche INRIA Rhoˆne-Alpes, 46 avenue Fe´lix Viallet, 38031 GRENOBLE Cedex
I n this section we shall give some results on the growth of powers of elements in Mp, which are modifications and localizations of results proved e.g. The main
![Figure 6: Recursive adaptive renaming algorithm (code for p i ) [13]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/11330810.283450/12.918.293.629.407.569/figure-recursive-adaptive-renaming-algorithm-code-p-i.webp)

![Figure 9: k -Obstruction-free adaptive M -renaming with M = min(2p − 1, p + k − 1) [36]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/11330810.283450/15.918.199.714.93.431/figure-obstruction-free-adaptive-m-renaming-m-min.webp)


