One and two-fiber orientation kinetic theories of fiber suspensions
Texte intégral
Figure


Documents relatifs
Dans cette thèse, nous proposerons d’une part des modèles mathématiques qui modélisent mieux la propagation du crapaud buffle, à l’aide de données statistiques collectées sur
Our aim is to show that noise has a regularizing effect on both the SDE (2) and the SPDE (1), in the sense that it provides results of existence, uniqueness and regularity
An adaptation of the notion of duality solutions, introduced for linear equations with discontinuous coefficients, leads to an existence result.. Uniqueness is obtained through
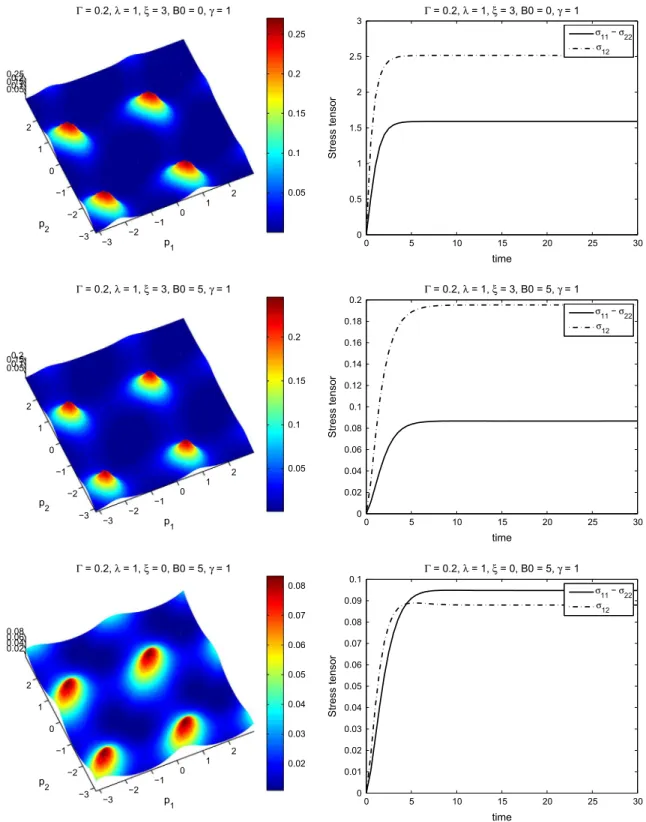
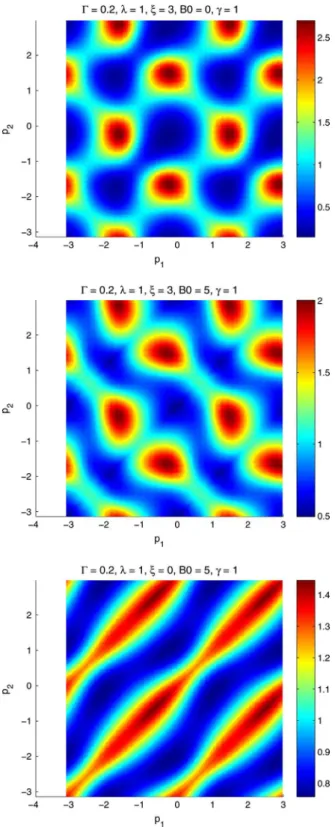
A new numerical strategy to compute steady solutions of the fiber orientation distribution in steady recirculating flows involving short fiber suspensions have
The main issue related to enriched kinetic theory descriptions lies in its curse of dimensionality, because generalized Fokker-Planck equations are defined in highly
In this paper, we study the Gevrey regularity of weak solutions for a class of linear and semi-linear kinetic equations, which are the linear model of spatially inhomogeneous
At present, the program in [4] leaves aside the compressible Euler limit of the Boltzmann equation, or the asymptotic regime leading to the compressible Navier-Stokes equations.
In this work, we have derived the incompressible Euler equations from the Boltz- mann equation in the case of the initial boundary value problem, for a class of boundary conditions