Microstructural-based analysis and modelling of the fatigue behaviour of cast Al-Si alloys
Texte intégral
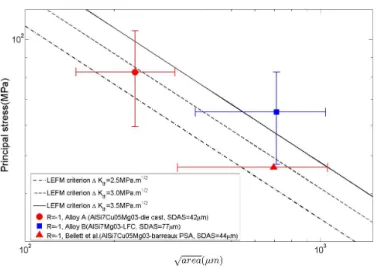
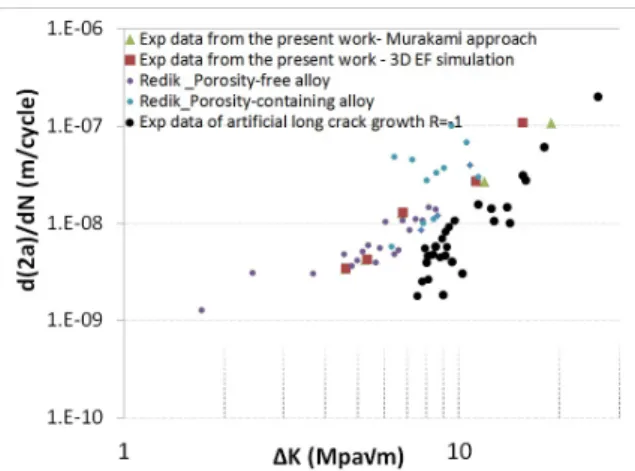
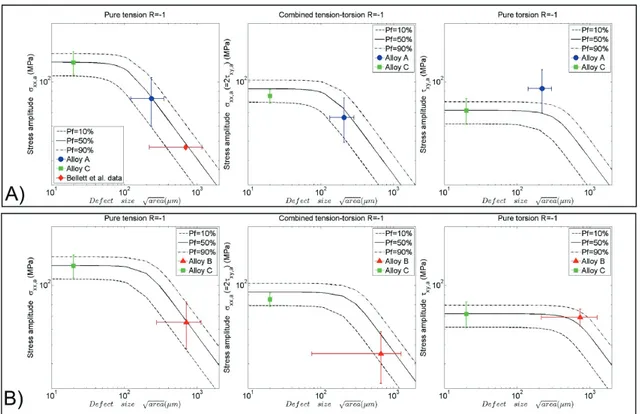
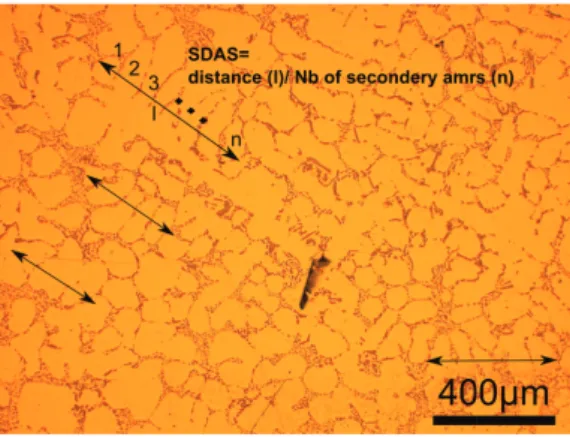
Figure



Documents relatifs
On the right side of the photo, the grain traces are clearly observed, whereas after the point 1 (Figure 6b), the fracture surface appearance change, change which is attributed to
The reasons for the outstanding performance of AI-Li alloys are manifold. It is argued that part of the improved crack growth resistance can be attributed to the
The opening normal stress applied to the slip band is not then relaxed by plastic deformation on secondary slip systems and remains very high, 1121 leading to the crack
From a scientific point of view the crack extension during the delay stage ad, the crack growth rate during the retardation stage (da/dN)D, the AKeff value after
The model predicts the evolutions of the plastic intensity factor under variable amplitude and non-proportional mixed mode conditions, and the plasticity rates pre- dicted by
The fact that specimens with artificial internal defects and those with surface artificial defects cycled in vacuum (no Region I) fall on the same curve tends to indicate that, for
The fatigue crack growth rate (FCGR) is shown as a function of crack length a, for tubular specimen with a horizontal notch and crack growth curves are shown in Fig.. A very
Quantitative analysis of the crack path was performed by characterizing the main crack and observing its interactions with different phases present in the