Minimal single linear functional observers for discrete-time linear systems
Texte intégral
Figure
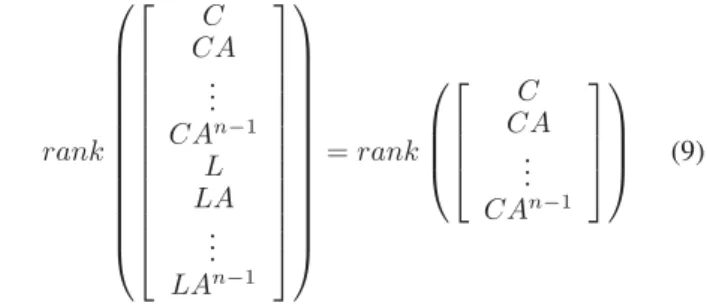

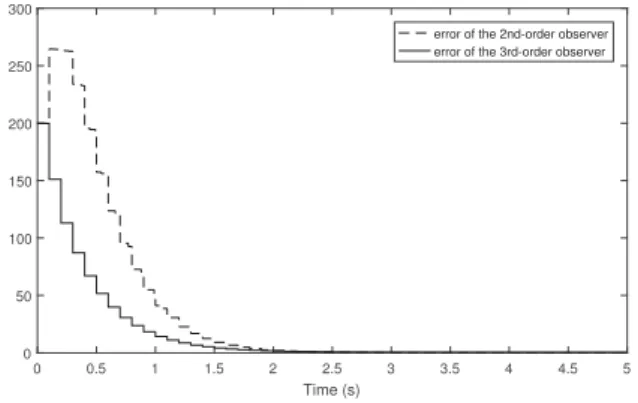
Documents relatifs
The purpose of this paper is to extend the main con- struction proposed for two dimensional systems in [Mazenc and Bernard, 2010]: we present a technique of construction of
For the sake of generality, we introduce a definition of interval observers for perturbed time-varying nonlinear systems with outputs containing noisy measurements of the state taken
Linear Parameter Varying systems theory has been mo- tivated by the gain scheduling approach which att- empts to provide a systematic methodology to design parameter-dependent
Linear Parameter Vary- ing systems theory has been motivated by the gain scheduling approach which attempts to provide a systematic methodology to design parameter-dependent
In section 3, under the assumption that the multiple model is locally detectable, sufficient conditions for the global exponential stability are derived in LMIs
Abstract— This paper deals with fast input-free partial state estimation for discrete-time LPV systems through functional observers.. The system inputs are assumed to be unknown
In order to reduce the number of these sampling instants, a dynamic scheduling algo- rithm optimizes, over a given sampling horizon, a sam- pling sequence depending on the system
In this paper, the expected real rate of return of the market portfolio falls less if expected inflation increases because of an increase in expected money growth than if it