Variable and Value Elimination in Binary Constraint Satisfaction via Forbidden Patterns
Texte intégral
Figure


Documents relatifs
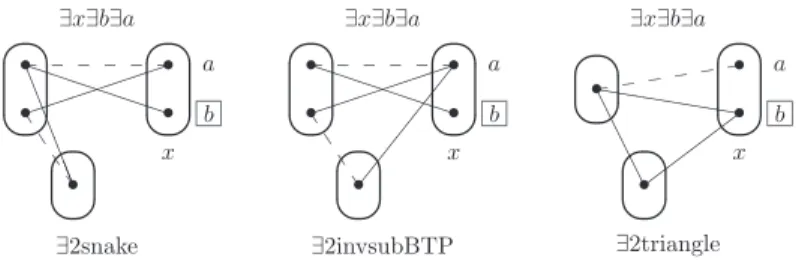
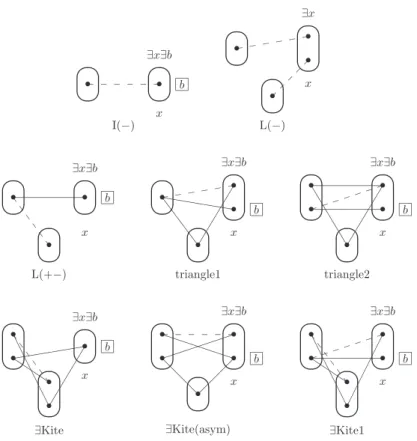
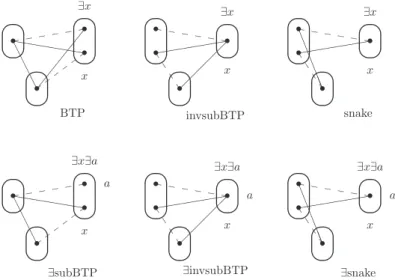
For example, as we will show later, the patterns snake and ∃snake shown in Figure 1 are both VE patterns, but the latter allows more variables to be eliminated since we only
The latter question leads to the notion of advantage of a random solution over the worst solution value. The issue here consists in ex- hibing “the tightest” possible lower bound ρ
We denote |Y | the set of irreducible π-primitive elements in P rim(A).. The proof of the previous results are straightforward, they follow from classical Weierstrass type results..
[r]
Let us denote by RG perm p the category of all p {permutation RG {modules. The following proposition generalizes to p {permutation modules a result which is well known for
Show that there exist entire functions of arbitrarily large order giving counterexamples to Bieberbach’s claim p.. Let f be an
Repeat the exer- cise in homology, for cor G×K H×K and tr G×K H×K (in homology, the hypothesis that G be finite can be supressed, but of course we need [G : H ] < ∞ for the
Write a detailled proof of the Cartan-Eilenberg double coset for- mula, using the hints given in the lecture..