An enhanced spatial smoothing technique with ESPRIT algorithm for direction of arrival estimation in coherent scenarios
Texte intégral
Figure
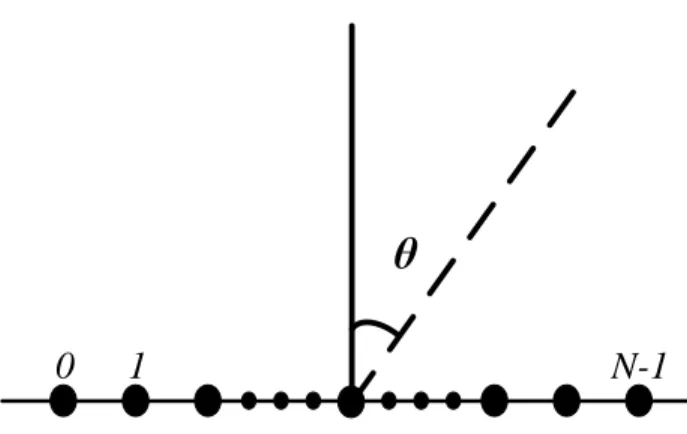
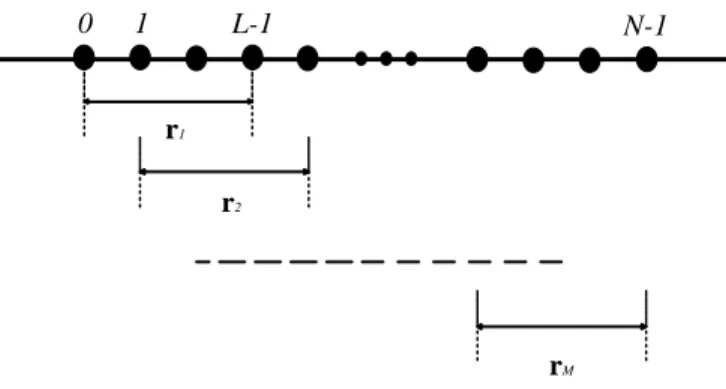
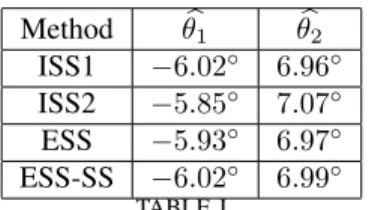
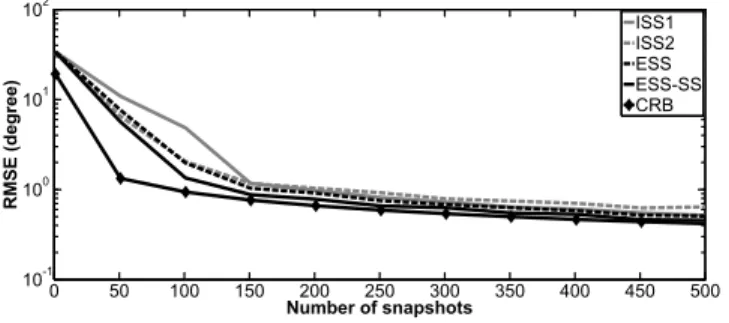
Documents relatifs
The recent references [BFG + 15] and [FBD15] provide asymptotic results for maximum likelihood approaches, and require that the smallest eigenvalue of the covariance matrix of
This heuristic argument can be transformed into a proof of the smoothing effect either by direct calculations (in the case of the free Schr¨odinger equation) or by means of
If there is indeed a correlation between the relative gene expression levels and the class, more genes should appear to be correlated in the experimental condition than in the
Accordingly, the paper evaluates the performance of the proposed approach in conjunction with a number of popular and widely- used recommendation algorithms in terms of their
SDWM is a metamodel that embeds the following significant features: (i) disassociating DW modeling from OLAP cube modeling; (ii) representing the spatiality in a
This paper proposes the integration of the spatial dimension into an ontology in order to enable experts in the maritime domain to specify rules governing abnormal ship
The ICCs from KSIRT are data-driven vi- sual representations of the relations between the latent di- mension and item responses, and they provide a conve- nient preliminary feedback
By using an energy method on the equation satisfied by some (higher order) derivative of the solution of the Landau equation, it is possible to prove that one derivative with respect