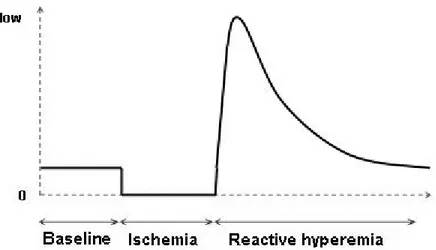
Reactive Hyperemia as endothelial function determinant using plethysmography methods
Texte intégral
Figure
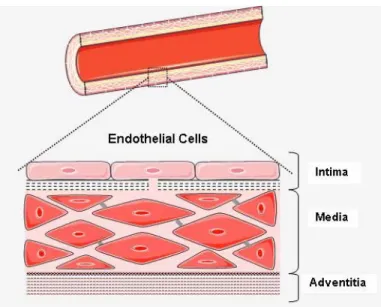
![Figure 2-2: Vascular remodeling agents: signals, sensors and mediators [2].](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/2174477.10220/15.918.240.732.292.637/figure-vascular-remodeling-agents-signals-sensors-and-mediators.webp)
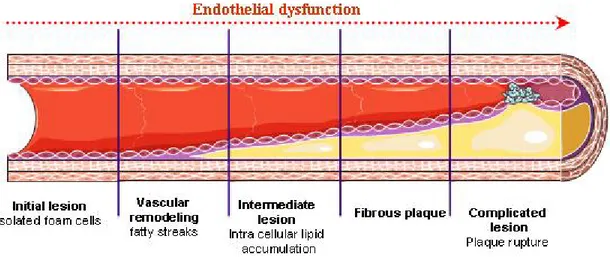
![Figure 2-3: The pathway of endothelial derived relaxing factor release [12-14].](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/2174477.10220/17.918.228.744.117.575/figure-pathway-endothelial-derived-relaxing-factor-release.webp)
![Table 2-2: Endothelial responses to relatively high and low hemodynamic shear stress [23]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/2174477.10220/22.918.163.809.408.953/table-endothelial-responses-relatively-high-hemodynamic-shear-stress.webp)
Documents relatifs
In the present study, we confirmed an important role of endothelial αENaC in endothelial cortical cell stiffness: both pharmacological inhibition and targeted genetic inactivation
In the context of cancer, the process of EndMT was identified in 2007 in melanoma and pancreatic tumor mouse model (Zeisberg et al., 2007) and critically involved in tumor
Suppose that a function f is analytic throughout the finite plane except for a finite number of singular points interior to a positively oriented simple closed contour C. Then,
In the present study we have performed energy flux measurements at the substrate location during reactive sputter deposition by means of an energy flux diagnostic (thermopile, 300
An additional sensitivity analysis, in which participants with factors potentially associated with a BP non-dipping profile (cardiovascular drug intake, clinical hypertension,
global approach (implicit scheme and Newton’s method) adaptive time step and modified Newton iterations (convergence monitoring). Newton-GMRES using the
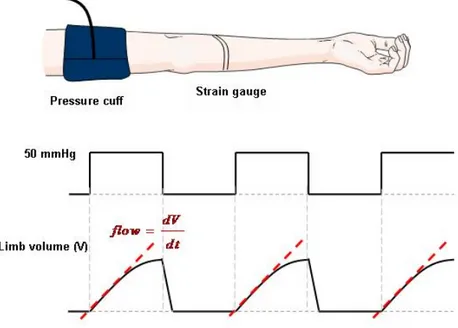
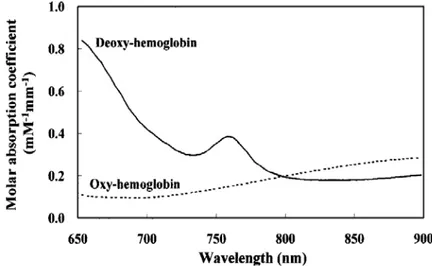
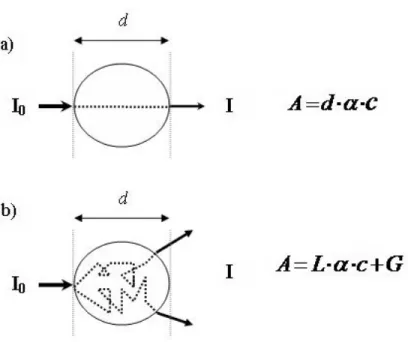
![Figure 2-10: The instrument design of a modular NIRS system by Wariar et al. BPF represents band-pass filter [37]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/2174477.10220/33.918.178.789.133.468/figure-instrument-design-modular-nirs-wariar-represents-filter.webp)