How to determine model Hamiltonians for strongly correlated materials
Texte intégral
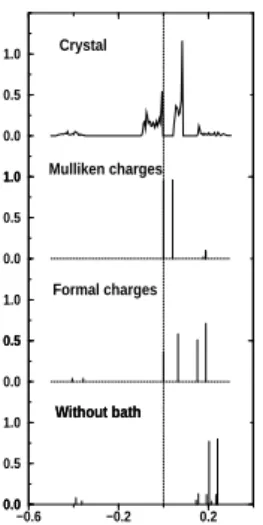
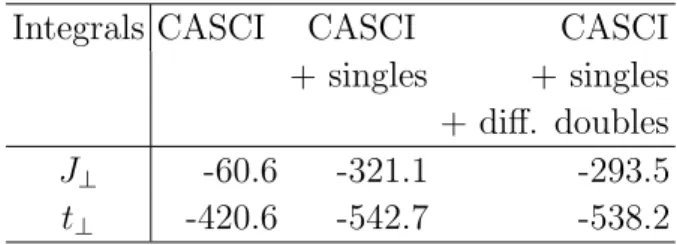
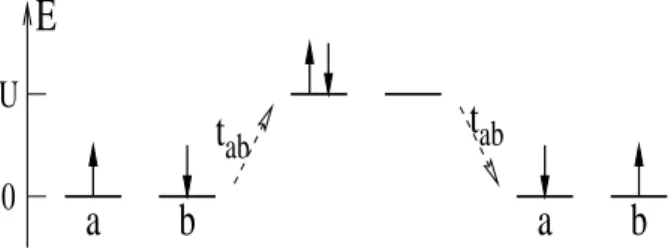
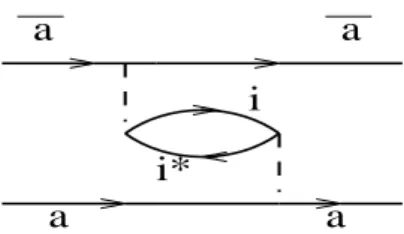
Figure
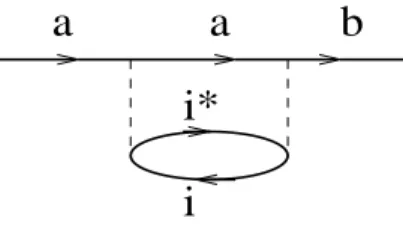
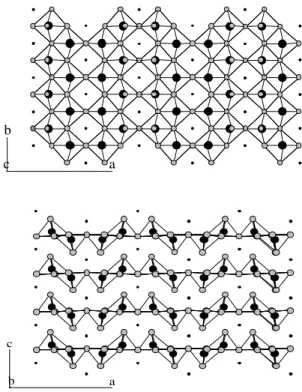
Documents relatifs
Figure 1 shows the pressure broadening and shifting cross sections as a func- tion of the kinetic energy for various vibrational bands for the S v (1) and O v (3) lines, as well as
Derivation of a frequency in- dependent criterion to determine the limp model validity for highly porous sound absorbing
This paper reports a number of aspects that include the following: the description of the methods for obtaining and treating the key parameters needed in crystallization models,
mixing. Solid state physics calculations have shown that such parabolic laws are valid in many cases [6] but not for all types of binary alloys, even when limited to
The Rouse modes under shear can then be used for a projection onto macroscopic Langevin equations for collective variables like concentration and stress tensor fluctuations..
One crucial aspect of our vote encryption verification constructions, and of electronic voting in general, is the proof that the vote encryption is well-formed, i.e. the proof that
In this study, the parameter FSI was compared to critical values obtained for different boundary conditions and porous thicknesses to give an estimation of the
In this lesson the students apply the FLE in order to calculate the expansion of space backwards from the current light horizon r lh.. The observable space is limited by the