Free vibrations of linear viscoelastic polymer cantilever beams
Texte intégral
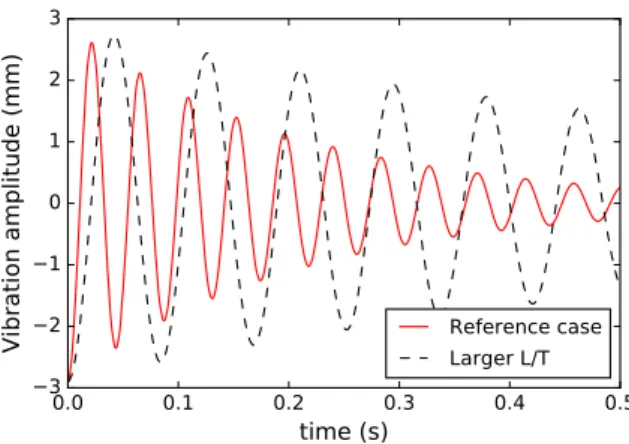
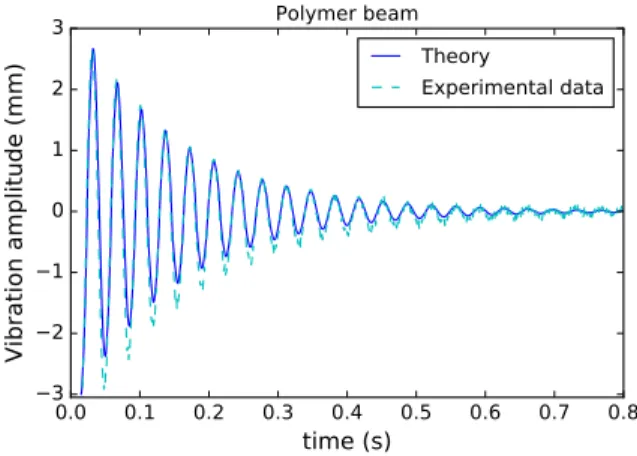
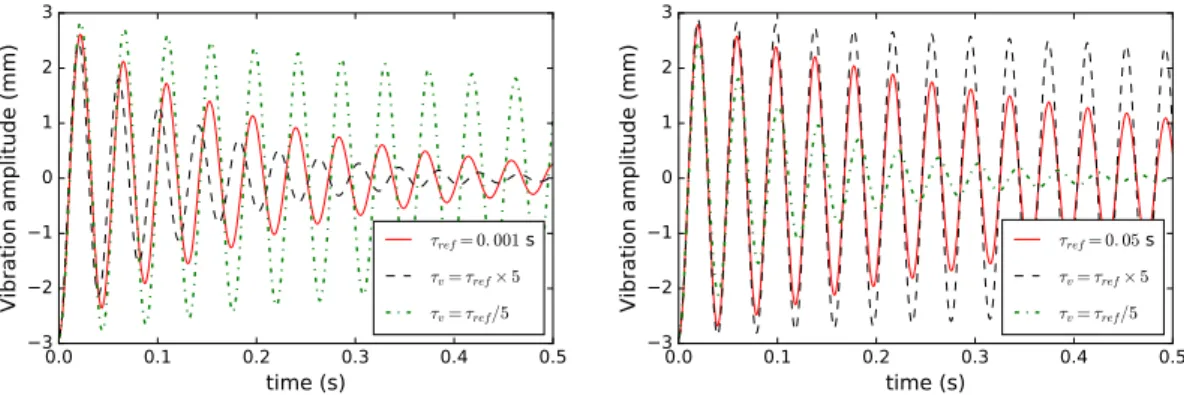
Figure

Documents relatifs
This paper deals with the evaluation of the collocation method, used in homogenization [7], by considering a more general approach to approximate eective relaxation or creep func-
In [30], Tanaka and Tani proved in 2003 the local existence for arbitrary initial data and global existence for sufficiently small initial data of a compressible Navier-Stokes flow
We have developed a nonlinear methodology based on the SolvOpt algorithm of Kappel & Kuntsevich (2000) to optimize the coefficients of the Zener viscoelastic model that
The incremental stress and strain constitutive equations are not restricted to isotropic materials and can be used to resolve complex boundary viscoelastic problems without
However, these methods have some drawbacks (i) in low frequency, the Fourier based IWC method suffers from resolution limitations; (ii) in practice, the beam response is composed
Separation of elastic waves in split Hopkinson bars using one-point strain measurements. Separation et reconstruction des andes dans les barres elastiques et
L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, émanant des
This paper deals with the evaluation of the collocation method, used in homogenization [7], by considering a more general approach to approximate effective relaxation or creep