Perception and human interaction for developmental learning of objects and affordances
Texte intégral
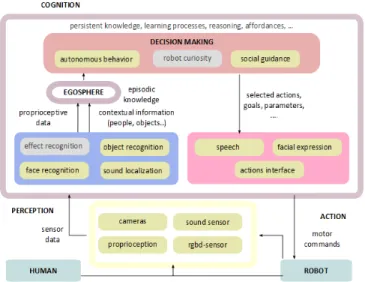
Figure



Documents relatifs
The first is the lack of a correlation (and, in some cases, computation) between the main components that are needed for impact assessment, the mission and its
Neeley & Barton accept the current evidence that the number of microburins (the waste product of the microburin technique) varies strongly among Epipalaeolithic
If a role represents the possibilities offered by an object to interact with it, the meth- ods of a role must be able to affect the core state of the objects they are roles of and
The section which follows discusses the potential for utilizing photovoltaic (solar cell) powered pumping systems to supply water over low lift regimes to small
Recientemente, el esfuerzo del proyecto <e-Aula> de investigación en e-learning se ha centrado en el desarrollo de un sistema para la evaluación de cómo las tecnologías
The pragmatic turn, which will be at the center of my interest hère, claims that in order to understand this constitutive character of language and in order to critically evaluate
In this paper we investigate the G-module structure of the universal enveloping algebra U(^) of the Lie algebra ^ of a simple algebraic group G, by relating its structure to that of
ficiently general to apply to all topological categories (strictly speaking, categories internal to the category of weak Hausdorff k-spaces).. as well as the more

