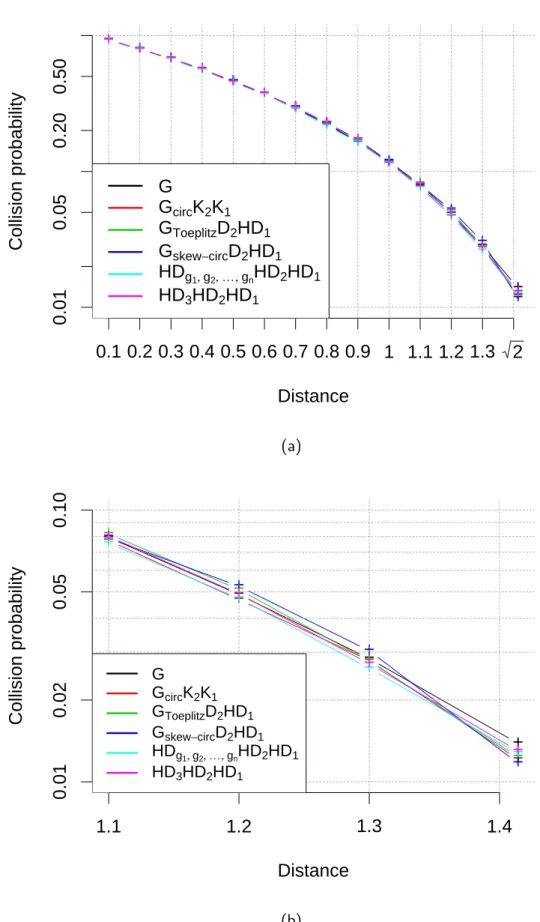
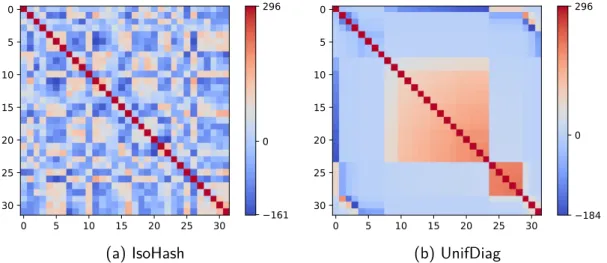
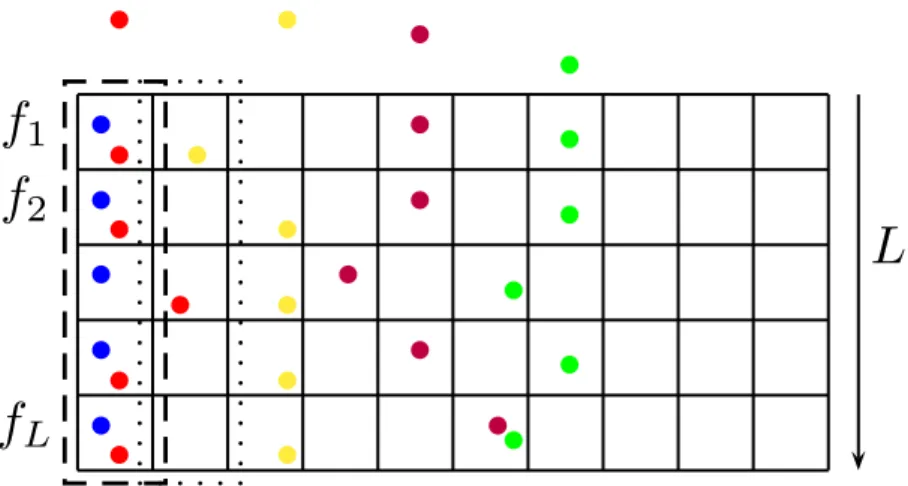
Contributions to unsupervised learning from massive high-dimensional data streams : structuring, hashing and clustering
Texte intégral
Figure



Documents relatifs
The Fast Incremental Model Tree (FIMT) proposed in [10], is an in- cremental algorithm for any-time model trees learning from evolving data streams with drift detection.. It is based
We also proposed a feature selection scheme adapted to hierarchical classifiers, which outperforms feature selec- tion strategies applied to the standard 1vs1 SVM classifier when
The time interval between the specified reference points on the input and output voltage waveforms, with the three-state output changing from either of the defined active levels (high
Not only are they affected by time pressure, but they also largely contribute to this trade-off, since shortening motor execution stages also increases the number of overt errors
The results suggested that the importance of surface cur- rents for analysing fishing activity from VMS data might de- pend upon the fishing gear, with a much higher impact on
In fact, we show that if the lifted Markov chain can not be initialized, and thus convergence needs to happen for all initial states on the expanded state space, while preserving
The objective of this study is to identify and un- derstand the contributions of collective moments of whole-group discussions for the construction of didactical pathways, based
Within the frameworks of learning in the limit of indexed classes of recursive languages from positive data and automatic learning in the limit of indexed classes of regular