TDMA scheduling strategies for vehicular ad hoc networks: from a distributed to a centralized approach
Texte intégral
Figure
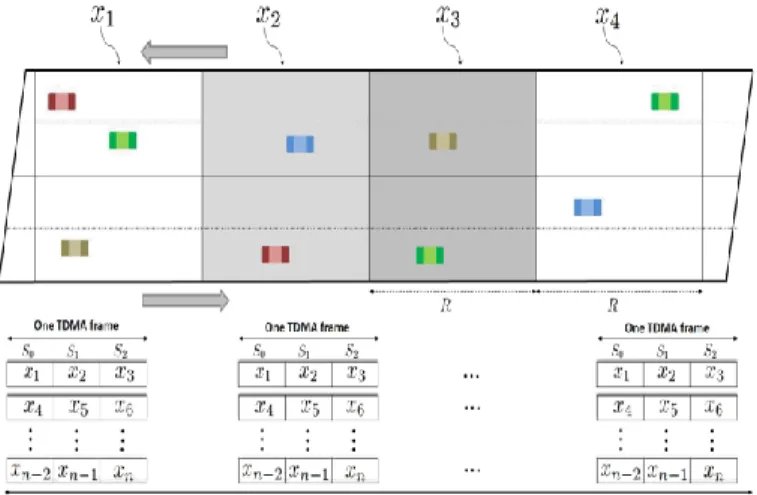

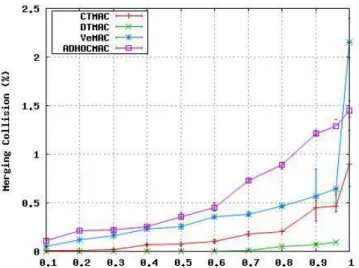
Documents relatifs
For this attack, two simulations have been executed (illustrating proto- cols robustness both on complete and social networks) to see the number.. probability 1 5 ) and the
In particular, thanks to the defined redundancy ratio metric, vehicles transmitters are able to dynamically adjust the probability of rebroadcast according to the
In this section, we evaluate our mechanism with different parameters to investigate the impact of the vehicle density, sensors sensitivity and percentage of equipped vehicles on
2) Impact of speed and arrival rate on the efficiency: Let us study now the efficiency of the clustering algorithm. The efficiency relies on the percentage of vehicles that acquire a
MEDAL makes use of both the moving directions of vehicles and the destination location to select the next-hop vehicle for forwarding data, and allows a node to make a
Fig. 2 gives an example for illustrating effective neighbor selection. Assume that a source vehicle A within the dotted circle receives a data packet from its left vehicles
This paper investigates the problem of designing and evaluating an autonomic and robust broadcasting protocol, which provides each node with the adequate strategy to determine if
In contrast, when we identified 389 compartment boundaries in treated cells that were positioned at loop domain anchors annotated in untreated cells (within 25kb), we found that