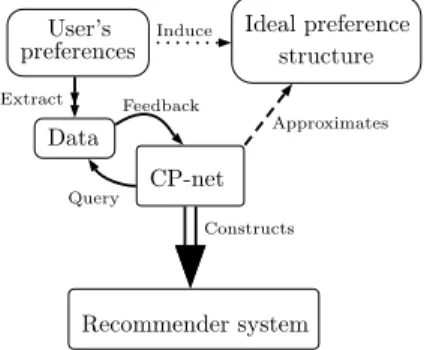
Query-based learning of acyclic conditional preference networks from contradictory preferences
Texte intégral
Figure


Documents relatifs
Comme nous nous int´eressons aux pr´ef´erences d’un groupe d’utilisateurs, nous allons ajouter des probabilit´es dans les tables de pr´ef´erences lo- cales afin de construire
We have described in this paper how it is possible to learn a probabilistic representation of the preferences of a group of users over a combinatorial domain, or how we can fine-
Moreover, the possibilistic representation is expressive (see [10] for an introductory survey), and can capture partial orders thanks to the use of symbolic weights, without
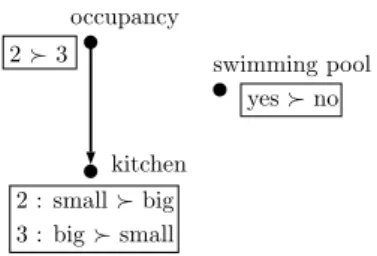
Since it is easy, and reasonable, to further impose that the learned CP-net has a digraph with a small degree k (see the experiments), and hence that m is in O(n k ), we finally get
The class C TREE is attribute-efficiently learnable from equivalence and membership queries over arbitrary out- come pairs: any concept ≻ in this class can be identified in
Dynamis of preferene systems We have onsidered xed aeptane graph and preferene lists.
(c) Bose S K, Geetharani K, Ramkumar V, Varghese B and Ghosh S 2010 Chemistry of Vanadaboranes: Synthesis, structures, and characterization of organovanadium sulfide clusters
By contrast, acyclic CP-nets are what is called attribute-efficiently learnable when both equivalence queries and membership queries are available: we indeed provide a