2D1/2 thermo-mechanical model of continuous casting using FEM
Texte intégral
Figure
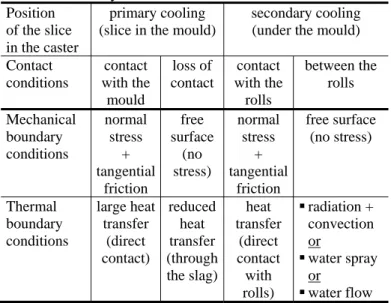
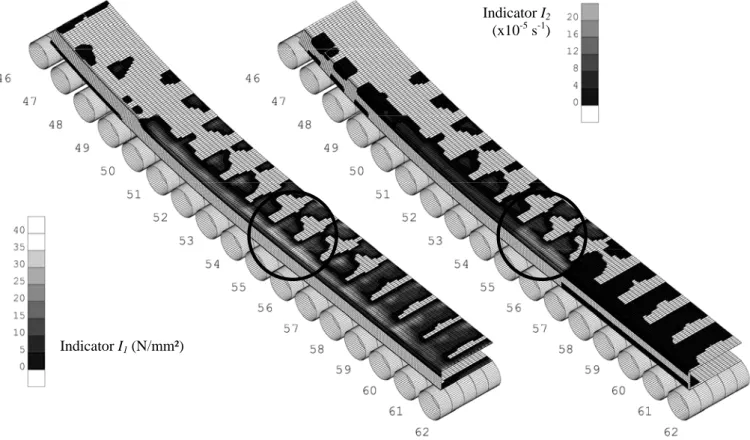
Documents relatifs
In papers as [10,12,15–20], the assemblage model, finite elements method and the two-scale asymptotic homogenization method are used to derive in one way or another the
The contact constraints are considered in this formulation using penalizing coefficients and Lagrange multipliers, penalizing the non-penetration restrictions violations in
From this it follows that the Necessitative mood must have been copied before the Hypothetical suffix entered the language, and consequently, if the connective glide prevalent in
In Section 3, we provide all necessary ingredients in order to prove our main result, which claims that the derivative of a parameterized mechanical contact problem with a
As a critical investigation of this scenario, we propose here a model to assess under which conditions the divergence of an ecological trait in two populations that are in sympatry is
Rough surfaces are squeezed from zero up to full contact, which enables us to compare the numerical results both with asperity based models at light pressures and with Persson’s
The problem is approached with a fluid energy of the second gradient form and a wall surface energy depending on the value of the fluid density at the contact.. From the virtual
This numerical method is used to predict the real contact area as a function of the contact force between rough surfaces starting from real shape of the surfaces that come in