Coupled temperature and strain rate effects on non-linear mechanical behaviour of amorphous polymers : Experimental characterisation and modelling of strain rate-temperature superposition
Texte intégral
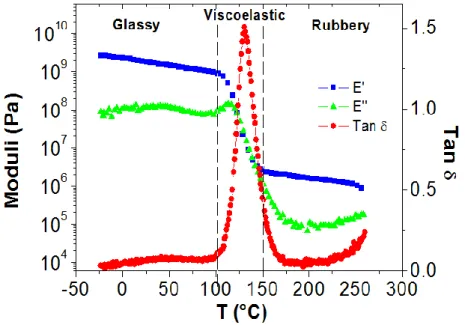
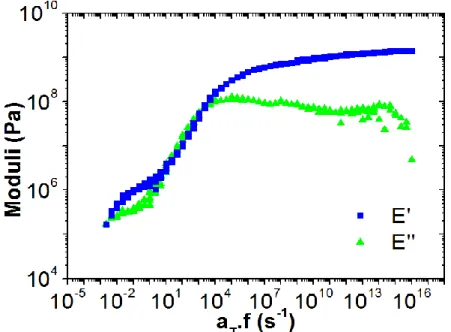
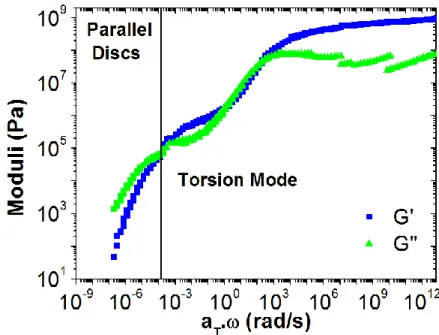
Figure



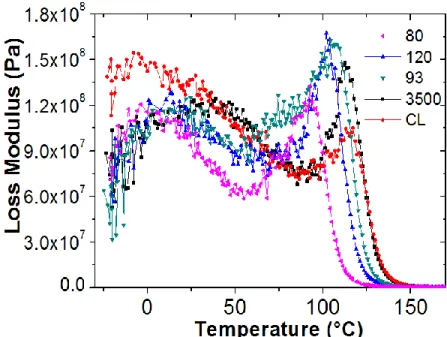
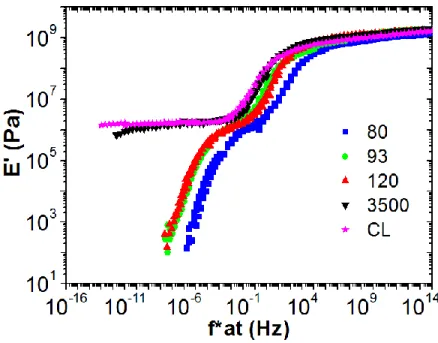
![Figure 3.3: Temperature dependence of the loss modulus for a PMMA at 1 Hz. [1]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/2974107.82875/40.918.258.665.728.989/figure-temperature-dependence-loss-modulus-pmma-hz.webp)
Documents relatifs
Nous montrons ici qu’une variante de la piste presque-périodique pour l’hypothèse de Riemann généralisée passe par une bonne connaissance des applications linéaires dont les
This Research Topic Ebook presents current research illustrating the depth and breadth of ongoing work in the field of flow and transformation in porous media through 15 papers by
This induced a reduction of the amount ofparticles with size greater than 20 mm but had almost no impact on the production of fines (amount ofparticles smaller than 2 mm).
Consensus guidelines for the optimal management of adverse events in newly diagnosed, transplant-ineligible patients receiving melpha- lan and prednisone in combination with
To study the mechanisms of initiation and propagation of ASB during a dynamic torsion test, we developed an experimental device to measure temperature by pyrometry: for
This study deals with the dynamic behaviour of metallic materials and in particular of titanium alloy TA6V. For high strain rates, we can notice the occurrence of
This work unifies recent results on descent algorithms for non-convex optimization for inverse problems with low-dimensional models in both finite and infinite dimension, such
These observations allow various domains to be defined in the strain rate - temperature plane, where the damaging process characteristics are different: a high strain rate / low