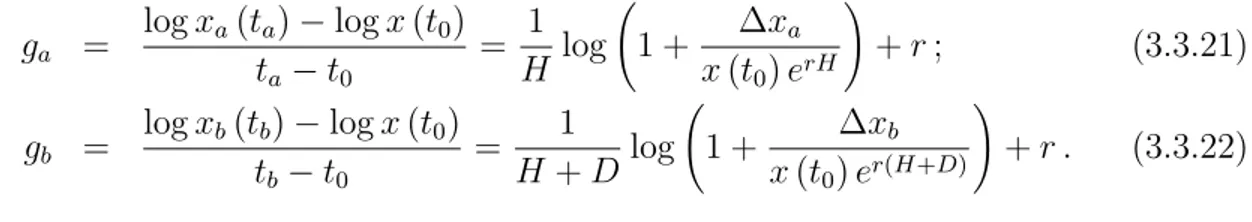Choice and Innovation
Texte intégral
Figure


Documents relatifs
Since, as in the case of the Nash equilibrium the proofs of existence of the equilibrium in choice lean on fixed point theory for correspondences, let us first recall some
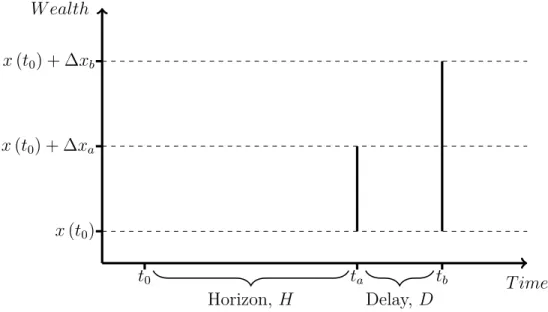
We obtain the value of the risk coefficient for which the problem of maximiz- ing the expectation of the portfolio return with a probabilistic risk function constraint is equivalent
To find the optimal equity share α(x), conditional on current wealth x, I define V (x), the expected intertemporal utility for wealth x. Since last period compound wealth may
Indeed since the mid- 1980s, lung cancer has overtaken breast cancer as the most common form of female cancer in the United States-the first country to show this
Moreover, as recalled in section 1, this geodesics condition is by no means necessary for the null-controllability of the heat equation. It is more relevant to the wave equation on M
• DR(mindestroy) uses weights that are associated with each assigned vari- able; when assigned, the weight of a variable v is initialised with the num- ber of values its
Now, there are essentially two possible axiom systems for mathematics : 1. second order classical logic with dependent choice... 2. Zermelo-Fraenkel set theory with the full axiom
Second order classical logic with the dependent choice axiom.. • Classical Zermelo-Fraenkel set theory with the axiom