Structural basis of alpha-amylase activation by chloride
Texte intégral
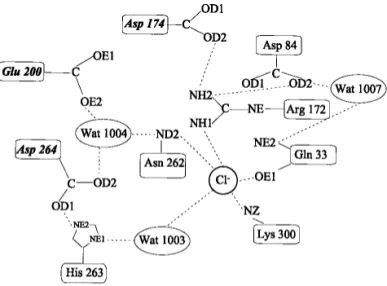
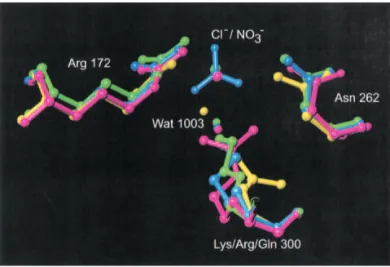
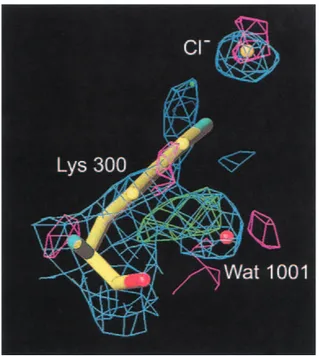
Figure
Documents relatifs
The reason why conflict resolution by FOLLOW set does not work nearly as well as one might wish is that it replaces the look-ahead of single item of rule N in a given LR state
This particular spelling does not occur in Zhu, where spellings khri tsan, khri tsan do occur.. The most com- mon spelling in Mdzod is khri tsan, although spellings
Our sensor outputs 10mv per degree centigrade so to get voltage we simply display the result of getVoltage().. delete the line temperature = (temperature - .5)
If I could have raised my hand despite the fact that determinism is true and I did not raise it, then indeed it is true both in the weak sense and in the strong sense that I
Recycling programs in St. John’s are inefficient, and are having a negative impact upon the
2. Duty to harmonize the special or regional conventions with the basic principles of this Convention. It is a convenient flexibility to allow the amendment of the application of
The conserved 7 DQAXXLR motif (X, any residue; Fig. 2b) of YlxH is found at the N terminus of the activator helix, with DQA forming a 3 10 -helical turn that locates at the
The parallel structure of the trees (as indicated by most links connecting one clade of each tree) suggests that YlxH has evolved largely in parallel to the 16S rRNA sequence,