Non-parametric identification of the non-homogeneous stress in high strain-rate uni-axial experiments
Texte intégral
Figure

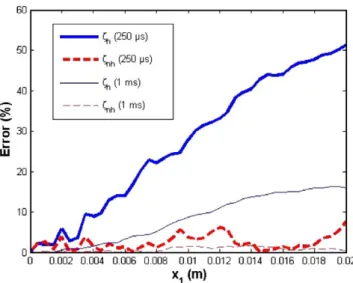

Documents relatifs
Theorem 2.15. The proof of the first identity is obvious and follows directly from the definition of the norm k · k 1,λ.. We start with the first idendity, whose proof is similar to
Due to the model uncertainties (for instance, errors induced by the introduction of simplified kinematical assumptions) and due to the data uncertainties related to the local
Algorithm 2 is similar to Algorithm 1, with the exception that the non-parametric estimate ˆ m r of the dynamical model is updated at each iteration r of the EM algorithm using LLR
This paper has introduced an original approach to the problem of identi cation of the velocity of under- ground regions from seismograms, based on the rep- resentation of
To assess performances of the combination of Fitted-Q with LWPR in environment with irrelevant inputs, we compute the average length of trajectories following the policy returned
investigation of the ordering kinetics, some reference measurements performed at the zone center (r point) pointed out that aging also induced an apparent broadening of the Bragg
In Section 3 it is shown that the problem of estimating parameter θ in (1) can be reduced to that of estimating the mean in a conditionally Gaussian distribution with a
In three different models: local and stochastic volatility, local correlation and hybrid local volatility with stochastic rates, this calibration boils down to the resolution of