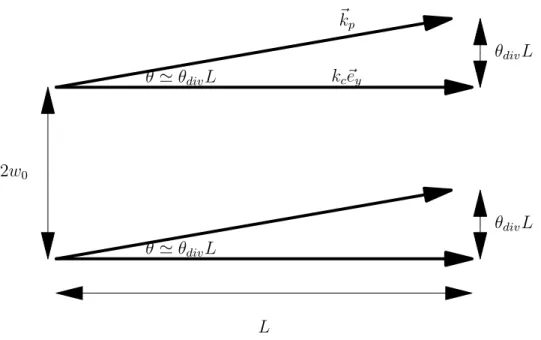
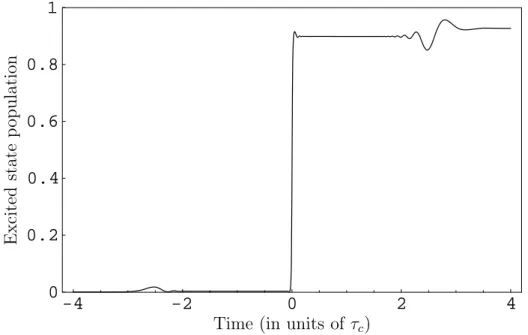
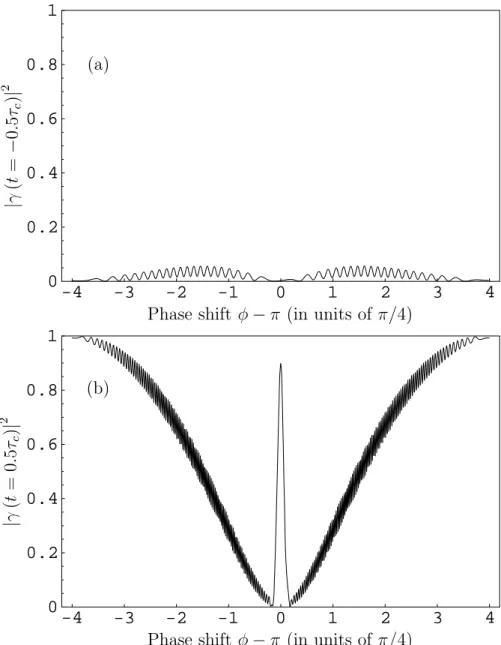
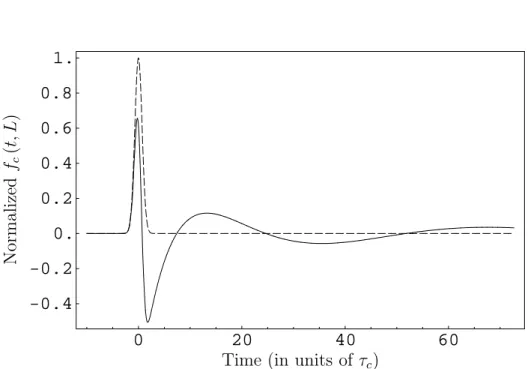
Effets de propagation dans des systèmes atomiques en régime d'impulsions longues et courtes : contrôle de la réponse optique
Texte intégral
Figure



Documents relatifs
Par ailleurs, le monde réel est riche de systèmes non linéaires multivariables, qui se caractérisent par la présence des interactions non linéaires et ce qui rend la conception des
A Q-matrix — an incidence matrix whose rows represent observable outcomes from assessment tasks and whose columns represent proficiency variables — provides the graphical structure
Once the adiabatic approximation is well justified in this rather involved framework, the accurate analysis, as well as the comparison when τ x is small, of the two reduced models
Dans le dernier chapitre nous développerons une méthode générale pour trai- ter l’interaction entre un champ quantique multimodes non-résonnant et un sys- tème atomique à
La répartition des germes dans notre étude reste à peu près la même pour toutes les tranches d’âge, à l’exception de Streptococcus B qu’on retrouve
Once the adiabatic approximation is well justified in this rather involved frame- work, the accurate analysis, as well as the comparison when τ x is small, of the two reduced
Abstract : Nous commen¸cons cette th` ese en donnant deux crit` eres de d´ e- tection d’intrication quantique, la Schr¨ odinger-Robertson partial transpose inequality qui peut ˆ
An infinitesimal increase of the volume ∆v brings an increase in p int , so that the piston moves until another equilibrium point with a bigger volume. On the other hand, a