Development of Reconfigurable Distributed Embedded Systems with a Model-Driven Approach
Texte intégral
Figure



Documents relatifs
This graphical editor corresponding to our SoSSec DSML (Fig. 6) could now be used by SoS security architects to model their SoS taking into account its specific characteristics
Lima et al. [ 72 ] verify UML 2.0 sequence diagrams by mapping each fragment into a process in PROMELA code where the send/receive event are specified by a communication
In order to verify model transformations with respect to behavioural equivalence we apply well-studied techniques based on the double pushout approach with borrowed context, for
In this section, we define a model transformation from a variant of UML statecharts [OMG09] to Petri nets [Pet80] using triple rules and application conditions.. Statecharts may
In particular, in research on ontologies, the notion of conservative extension has been cited from the algebraic specification literature (e.g. [25]) und used for the notion of
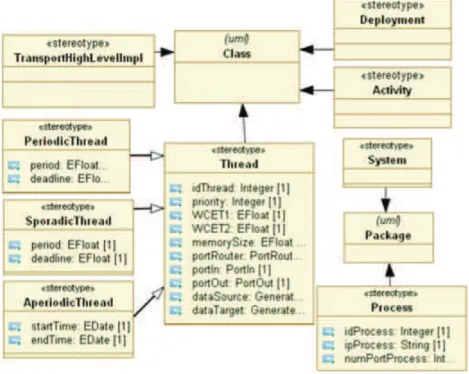
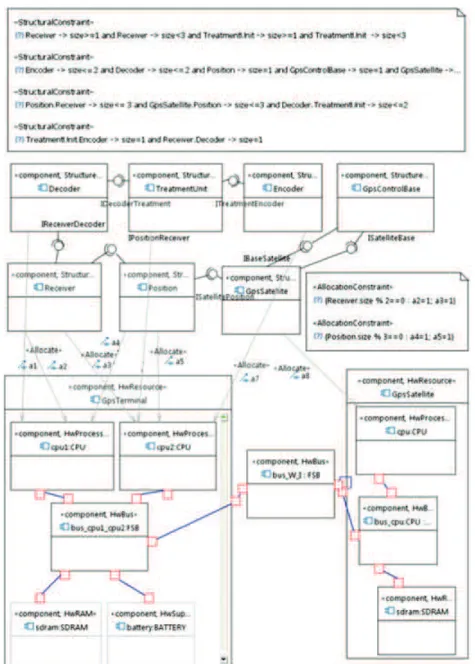
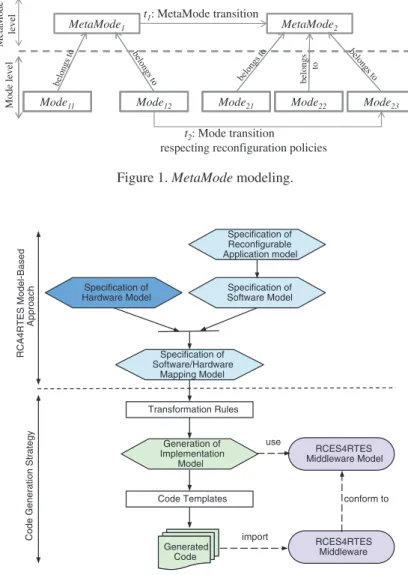
This application case uses the Architecture Analysis & Design Language (AADL) metamodel [47] and shows that a model-driven measurement approach is better than a document-
Aphanomyces euteiches cell wall fractions containing novel glucan-chitosaccharides induce defense genes and nuclear calcium oscillations in the plant host Medicago truncatula...
Le document 6 est un apport, toujours théorique mais en vue d'une application pragmatique, sur des mécanismes permettant de créer des milieux a-didactiques (ou à