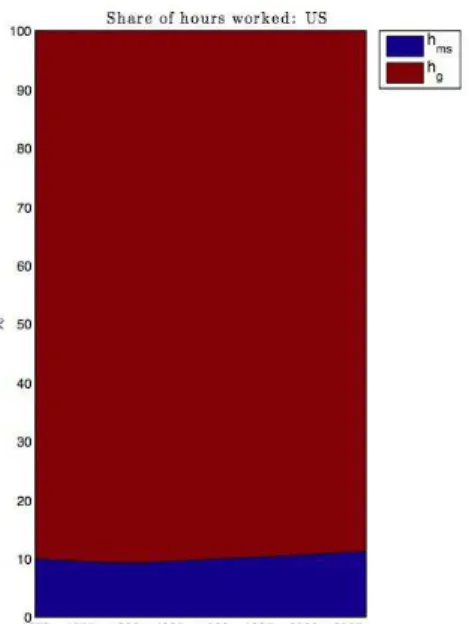
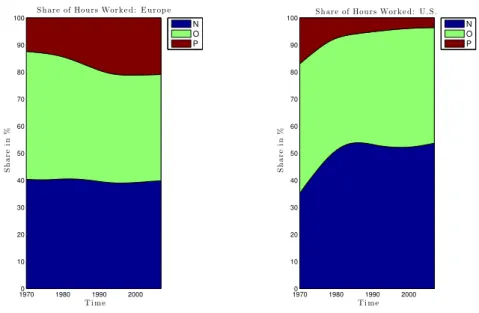
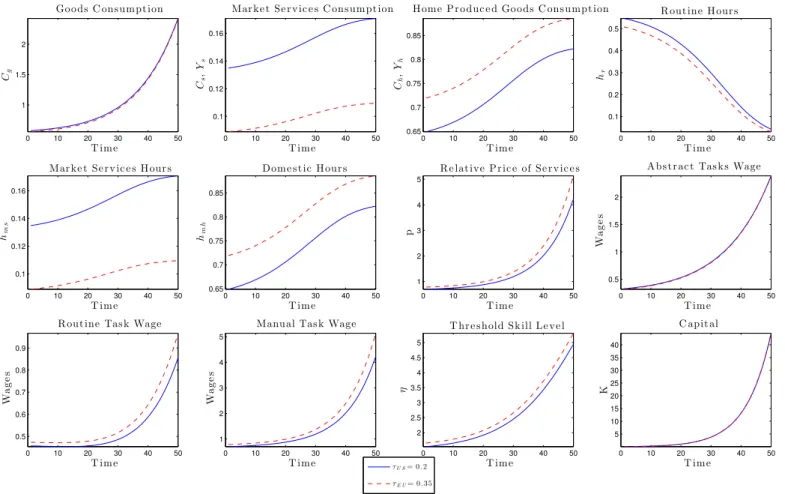
Structural Transformation and Labor Market Polarization: The Role of Productivity and Taxation
Texte intégral
Figure




Documents relatifs
[*** Treatments IDIR―When participant C makes his/her decision, he/she is informed of the groups (red or blue) of participants A and
The variables used to capture the employment situation during this crisis period are: (i) lower wages, a binary variable which takes the value 1 when the worker suffers from
Then, a tighter environmental tax increases the steady-state unemployment rate, whatever the source of pollution (physical capital or final output) and more frictions on labor
This means that immigrants with a degree from their country of origin compensate for the lack of human capital acquired in France by mobilising their social network to integrate
In the shipping industry, due to the overall use of international manning, the unit labor cost also depends on the standards of living in the country where the seafarer lives,
Sim- ilar to these models, ours allows to study the effects of early retirement transfers and aging on labor force participation but we find that these two shocks are insufficient
The comparison between Tables 1 and 2 suggest that, in the face of job competition, a scenario combining substantial tax rebates for minimum wage workers with much smaller
There is no shortage of housekeepers in France and, in this context, managers also adopt other practices that border on illegality: paying wages according to objectives (number