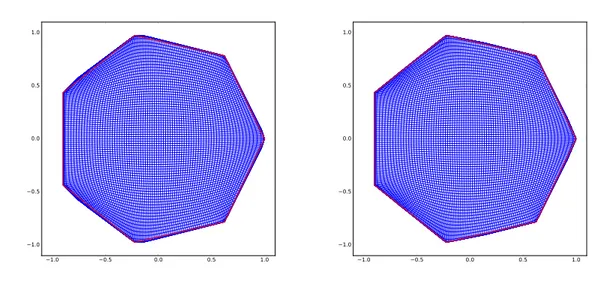
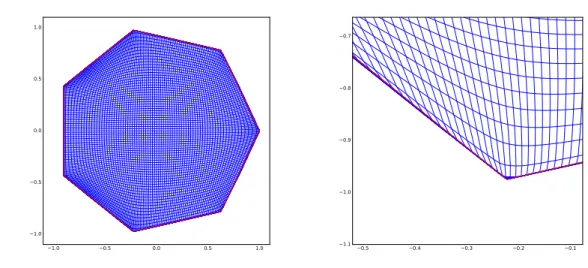
Minimal convex extensions and finite difference discretisation of the quadratic Monge–Kantorovich problem
Texte intégral
Figure
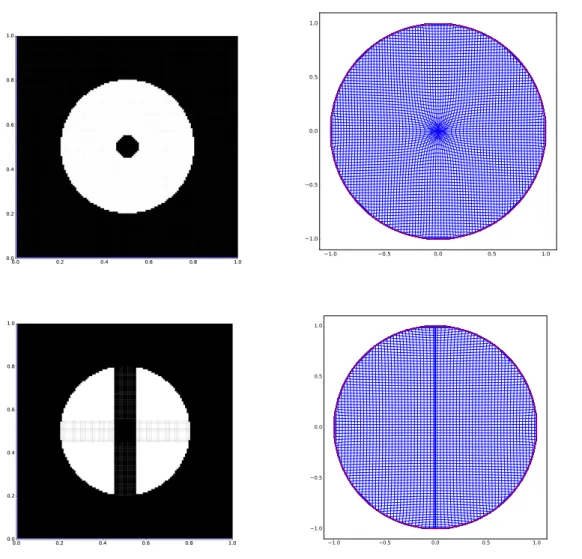
![Figure 3: Error E[x] when mapping a square to a disc. The plain implementation of (36) yields](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/2641408.59563/22.918.153.741.111.336/figure-error-mapping-square-disc-plain-implementation-yields.webp)
Documents relatifs
Instead of monotonicity and consistency of the scheme, the proof re- lies on three ingredients : specific properties of the LBR discretization of the Monge-Ampère operator
The Monge-Kantorovich problem is revisited by means of a variant of the saddle-point method without appealing to cyclical c -monotonicity and c -conjugates.. One gives new proofs of
In this article, we propose a generalization of the classical finite difference method suitable with the approximation of solutions in subspaces of the Sobolev spaces H −s , s >
Based on this idea, we define, in this paper, a Finite Di ff erence Element Method concept and we present a very simple four nodes quadrangular Finite Di ff erence Element
The existence of finite degree matching networks that can achieve the optimal reflection level in a desired frequency band when plugged on to the given load is discussed..
We present a general method, based on conjugate duality, for solving a con- vex minimization problem without assuming unnecessary topological restrictions on the constraint set..
As regards the most basic issue, namely (DG) pertaining to the question whether duality makes sense at all, this is analyzed in detail — building on a lot of previous literature —
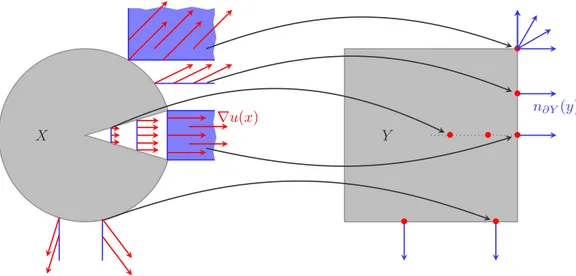
A new abstract characterization of the optimal plans is obtained in the case where the cost function takes infinite values.. It leads us to new explicit sufficient and